Combination of natural polyphenols with a precursor of NAD+ and a TLR2/6 ligand lipopeptide protects mice against lethal γ radiation
- PMID: 35599107
- PMCID: PMC10006514
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.05.005
Combination of natural polyphenols with a precursor of NAD+ and a TLR2/6 ligand lipopeptide protects mice against lethal γ radiation
Abstract
Introduction: Effective agents that could confer long-term protection against ionizing radiation in vivo would have applications in medicine, biotechnology, and in air and space travel. However, at present, drugs that can effectively protect against lethal ionizing radiations are still an unmet need.
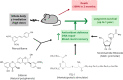
Objective: To investigate if combinations of natural polyphenols, known for their antioxidant potential, could protect against ionizing radiations.
Methods: Plant-derived polyphenols were screened for their potential ability to confer radioprotection to mice given a lethal whole-body γ radiation (137Cs) dose expected to kill 50% of the animals in 30 days. Telomere and centromere staining, Q-FISH and comet assays were used to investigate chromosomal aberration, micronuclei formation and DNA breaks. Molecular oxidations were investigated by enzyme immunoassays and UPLC-MS/MS. RT-PCR, western blotting and siRNA-induced gene silencing were used to study signaling mechanisms and molecular interactions.
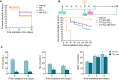
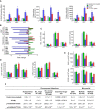
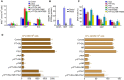
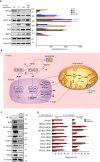
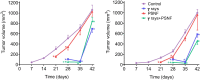
Results: The combination of pterostilbene (PT) and silibinin (SIL) was the most effective against γ-irradiation, resulting in 100% of the mice surviving at 30 days and 20% survival at one year. Treatment post γ-irradiation with two potential radiomitigators nicotinamide riboside (NR, a vitamin B3 derivative), and/or fibroblast-stimulating lipoprotein 1 (FSL1, a toll-like receptor 2/6 agonist), did not extend survival. However, the combination of PT, SIL, NR and FSL1 achieved a 90% survival one year post γ-irradiation. The mechanism involves induction of the Nrf2-dependent cellular antioxidant defense, reduction of NF-kB signaling, upregulation of the PGC-1α/sirtuins 1 and 3 axis, PARP1-dependent DNA repair, and stimulation of hematopoietic cell recovery. The pathway linking Nrf2, sirtuin 3 and SOD2 is key to radioprotection. Importantly, this combination did not interfere with X-ray mediated killing of different tumor cells in vivo.
Conclusion: The combination of the radioprotectors PT and SIL with the radiomitigators NR and FSL1 confer effective, long-term protection against γ radiation in vivo. This strategy is potentially capable of protecting mammals against ionizing radiations.
Keywords: Ionizing radiations; NAD(+) precursors; Natural polyphenols; Radioprotection; Toll-like receptor 2/6 ligands.
Copyright © 2023. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CBLB613: a TLR 2/6 agonist, natural lipopeptide of Mycoplasma arginini , as a novel radiation countermeasure.Radiat Res. 2012 May;177(5):628-42. doi: 10.1667/rr2657.1. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Radiat Res. 2012. PMID: 22175300
-
Prevention and mitigation of acute radiation syndrome in mice by synthetic lipopeptide agonists of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2).PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033044. Epub 2012 Mar 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479357 Free PMC article.
-
The Toll-Like Receptor 2/6 Agonist, FSL-1 Lipopeptide, Therapeutically Mitigates Acute Radiation Syndrome.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 11;7(1):17355. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17729-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29230065 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation Protection and Mitigation by Natural Antioxidants and Flavonoids: Implications to Radiotherapy and Radiation Disasters.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018;11(4):285-304. doi: 10.2174/1874467211666180619125653. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29921213 Review.
-
Radioprotective Role of Natural Polyphenols: From Sources to Mechanisms.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(1):30-39. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210419095829. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 33874875 Review.
Cited by
-
Polyphenols and metabolism: from present knowledge to future challenges.J Physiol Biochem. 2024 Aug;80(3):603-625. doi: 10.1007/s13105-024-01046-7. Epub 2024 Oct 8. J Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39377969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of dietary ingredients on radioprotection and radiosensitization: a comprehensive review.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2396558. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2396558. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39320122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotinamide riboside intervention alleviates hematopoietic system injury of ionizing radiation-induced premature aging mice.Aging Cell. 2023 Nov;22(11):e13976. doi: 10.1111/acel.13976. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Aging Cell. 2023. PMID: 37650560 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear and Radiological Emergencies: Biological Effects, Countermeasures and Biodosimetry.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 31;11(6):1098. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061098. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35739995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting Polyphenol-Mediated Redox Reorientation in Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 12;15(12):1540. doi: 10.3390/ph15121540. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36558995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

