Compartmentalization and transporter engineering strategies for terpenoid synthesis
- PMID: 35599322
- PMCID: PMC9125818
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-022-01819-z
Compartmentalization and transporter engineering strategies for terpenoid synthesis
Abstract
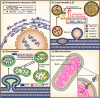
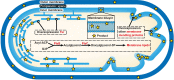
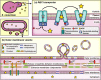
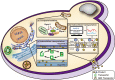
Microbial cell factories for terpenoid synthesis form a less expensive and more environment-friendly approach than chemical synthesis and extraction, and are thus being regarded as mainstream research recently. Organelle compartmentalization for terpenoid synthesis has received much attention from researchers owing to the diverse physiochemical characteristics of organelles. In this review, we first systematically summarized various compartmentalization strategies utilized in terpenoid production, mainly plant terpenoids, which can provide catalytic reactions with sufficient intermediates and a suitable environment, while bypassing competing metabolic pathways. In addition, because of the limited storage capacity of cells, strategies used for the expansion of specific organelle membranes were discussed. Next, transporter engineering strategies to overcome the cytotoxic effects of terpenoid accumulation were analyzed. Finally, we discussed the future perspectives of compartmentalization and transporter engineering strategies, with the hope of providing theoretical guidance for designing and constructing cell factories for the purpose of terpenoid production.
Keywords: Compartmentalization; Metabolic engineering; Terpenoids; Transporter.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32021005/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- JUSRP52019A/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- JUSRP121010/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- JUSRP221013/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- 2018YFA0900300/National Key R&D Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

