Age-related topographic map of magnetic resonance diffusion metrics in neonatal brains
- PMID: 35599634
- PMCID: PMC9435001
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.25956
Age-related topographic map of magnetic resonance diffusion metrics in neonatal brains
Abstract
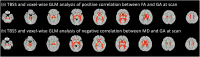
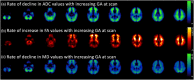
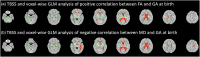
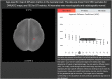
Accelerated maturation of brain parenchyma close to term-equivalent age leads to rapid changes in diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) metrics of neonatal brains, which can complicate the evaluation and interpretation of these scans. In this study, we characterized the topography of age-related evolution of diffusion metrics in neonatal brains. We included 565 neonates who had MRI between 0 and 3 months of age, with no structural or signal abnormality-including 162 who had DTI scans. We analyzed the age-related changes of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values throughout brain and DTI metrics (fractional anisotropy [FA] and mean diffusivity [MD]) along white matter (WM) tracts. Rate of change in ADC, FA, and MD values across 5 mm cubic voxels was calculated. There was significant reduction of ADC and MD values and increase of FA with increasing gestational age (GA) throughout neonates' brain, with the highest temporal rates in subcortical WM, corticospinal tract, cerebellar WM, and vermis. GA at birth had significant effect on ADC values in convexity cortex and corpus callosum as well as FA/MD values in corpus callosum, after correcting for GA at scan. We developed online interactive atlases depicting age-specific normative values of ADC (ages 34-46 weeks), and FA/MD (35-41 weeks). Our results show a rapid decrease in diffusivity metrics of cerebral/cerebellar WM and vermis in the first few weeks of neonatal age, likely attributable to myelination. In addition, prematurity and low GA at birth may result in lasting delay in corpus callosum myelination and cerebral cortex cellularity.
Keywords: diffusion tensor imaging; diffusion-weighted imaging; magnetic resonance imaging; neonates.
© 2022 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
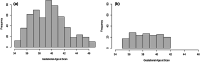
References
-
- Barkovich, A. J. , Miller, S. , Bartha, A. , Newton, N. , Hamrick, S. , Mukherjee, P. , Glenn, O. , Xu, D. , Partridge, J. , & Ferriero, D. (2006). MR imaging, MR spectroscopy, and diffusion tensor imaging of sequential studies in neonates with encephalopathy. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 27(3), 533–547. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belli, G. , Busoni, S. , Ciccarone, A. , Coniglio, A. , Esposito, M. , Giannelli, M. , Mazzoni, L. N. , Nocetti, L. , Sghedoni, R. , & Tarducci, R. (2016). Quality assurance multicenter comparison of different MR scanners for quantitative diffusion‐weighted imaging. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 43(1), 213–219. - PubMed
-
- Brissaud, O. , Amirault, M. , Villega, F. , Periot, O. , Chateil, J. , & Allard, M. (2010). Efficiency of fractional anisotropy and apparent diffusion coefficient on diffusion tensor imaging in prognosis of neonates with hypoxic‐ischemic encephalopathy: A methodologic prospective pilot study. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 31(2), 282–287. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cauley, K. A. , & Filippi, C. G. (2014). Apparent diffusion coefficient histogram analysis of neonatal hypoxic‐ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatric Radiology, 44(6), 738–746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

