Nanomaterials-based sensors for the detection of COVID-19: A review
- PMID: 35599642
- PMCID: PMC9110902
- DOI: 10.1002/btm2.10305
Nanomaterials-based sensors for the detection of COVID-19: A review
Abstract
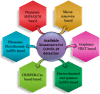
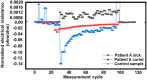
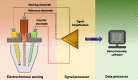
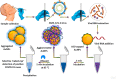
With the threat of increasing SARS-CoV-2 cases looming in front of us and no effective and safest vaccine available to curb this pandemic disease due to its sprouting variants, many countries have undergone a lockdown 2.0 or planning a lockdown 3.0. This has upstretched an unprecedented demand to develop rapid, sensitive, and highly selective diagnostic devices that can quickly detect coronavirus (COVID-19). Traditional techniques like polymerase chain reaction have proven to be time-inefficient, expensive, labor intensive, and impracticable in remote settings. This shifts the attention to alternative biosensing devices that can be successfully used to sense the COVID-19 infection and curb the spread of coronavirus cases. Among these, nanomaterial-based biosensors hold immense potential for rapid coronavirus detection because of their noninvasive and susceptible, as well as selective properties that have the potential to give real-time results at an economical cost. These diagnostic devices can be used for mass COVID-19 detection to understand the rapid progression of the infection and give better-suited therapies. This review provides an overview of existing and potential nanomaterial-based biosensors that can be used for rapid SARS-CoV-2 diagnostics. Novel biosensors employing different detection mechanisms are also highlighted in different sections of this review. Practical tools and techniques required to develop such biosensors to make them reliable and portable have also been discussed in the article. Finally, the review is concluded by presenting the current challenges and future perspectives of nanomaterial-based biosensors in SARS-CoV-2 diagnostics.
Keywords: COVID‐19; SARS‐CoV‐2; biosensors; coronavirus sensor; nanomaterial‐based biosensors; pandemic; point of care diagnosis.
© 2022 The Authors. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

