Emerging threat of drug-resistant tuberculosis and trends in the era of COVID-19: A descriptive study from northwestern Nigeria
- PMID: 35599722
- PMCID: PMC9110314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jctube.2022.100319
Emerging threat of drug-resistant tuberculosis and trends in the era of COVID-19: A descriptive study from northwestern Nigeria
Abstract
Background: Mycobacterium tuberculosis with resistance to first line and second line anti tuberculous drugs is a serious setback in the treatment of tuberculosis (TB). The COVID-19 pandemic constitutes a serious threat that could unwind the recent gains made thus far in the control of tuberculosis. This study aims to explore the pattern of drug resistant tuberculosis (DRTB) in our institution. We also aimed to explore the changing trends of TB in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: This descriptive study included all DRTB patients admitted and managed in the hospital between January 2018 and December 2020. We compare TB case detection in the facility before and after COVID-19 pandemic. Drug susceptibility testing were expressed as frequencies and percentages.
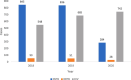
Results: The study found that there was 66.03%, 45.09% and 77.78% drop in case detection of drug-sensitive TB (DSTB), DRTB and Fluoroquinolone (FQ) resistant TB respectively in the year 2020 compared to 2019. The drop in cases was similar when the year 2020 was compared to 2018. Among the 132 patients in the cohort, resistance to isoniazid, fluoroquinolones and second-line injectable agents were reported as 23.48%, 12.88%, and 31.06% respectively.
Conclusion: We question the potential reason why a drop in tuberculosis cases was observed in the year 2020 and we alert the Nigerian authorities that COVID-19 control efforts going hand-in-hand with intensified TB case finding and surveillance efforts and initiating proper TB treatment for persons with active TB are urgently needed.
Keywords: COVID-19; Drug-resistant TB; Nigeria; Tuberculosis.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- G. Sotgiu, G. Sulis, and A. Matteelli Tuberculosis—A world health organization perspective Tuberculosis and Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infections, (2017), pp. 211-228.
-
- Federal Republic of Nigeria Report: First National TB Prevalence Survey, 2012, Nigeria 2012.
-
- WHO, Global tuberculosis report 2020: executive summary, 2020.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources