Predictive Biomarkers in Thyroid Cancer
- PMID: 35600349
- PMCID: PMC9120826
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.901004
Predictive Biomarkers in Thyroid Cancer
Abstract
In molecular pathology, predictive biomarkers identify which patients are likely to respond to targeted drugs. These therapeutic agents block specific molecules directly involved in cancer growth, dedifferentiation and progression. Until few years ago, the only targeted drugs available for advanced thyroid cancer included multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitors, mainly targeting the MAPK pathway and the angiogenic signaling. The administration of these drugs does not necessarily require a molecular characterization of tumors to assess the presence of predictive alterations. However, the availability of new selective targeted drugs for thyroid cancer patients is changing the diagnostic strategies for the molecular characterization of these tumors. The search for targetable alterations can be performed directly on tumor tissue by using a variety of methodologies, depending also on the number and type of alterations to test (i.e. single nucleotide variation or gene rearrangement). Herein, a comprehensive review of the currently available targeted treatments for thyroid cancer, related predictive markers and testing methodologies is provided.
Keywords: molecular marker; molecular pathology; predictive marker; targeted therapy; thyroid cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Macerola, Poma, Vignali, Proietti, Ugolini, Torregrossa, Basolo, Elisei, Santini and Basolo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
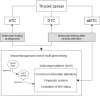
References
-
- Lloyd R, Osamura R, Kloppel G, Rosai J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs. 4th Ed. Lyon, France: IARC Press; (2017).
-
- Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, et al. . 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients With Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid (2016) 26:1–133. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

