Systemically Silencing Long Non-coding RNAs Maclpil With Short Interfering RNA Nanoparticles Alleviates Experimental Ischemic Stroke by Promoting Macrophage Apoptosis and Anti-inflammatory Activation
- PMID: 35600488
- PMCID: PMC9120540
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.876087
Systemically Silencing Long Non-coding RNAs Maclpil With Short Interfering RNA Nanoparticles Alleviates Experimental Ischemic Stroke by Promoting Macrophage Apoptosis and Anti-inflammatory Activation
Abstract
Background: Maclpil is a proinflammatory long non-coding RNA highly expressed on monocyte-derived macrophages in the ischemic brain. This study investigated the impact and the mechanisms of systemically delivering nanoparticle Maclpil short interfering RNA (siRNA) on experimental ischemic stroke in a mouse model.
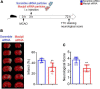
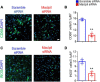
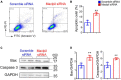
Methods: Ischemic stroke (focal cerebral ischemia) was induced in male C57BL/6 mice through the middle cerebral artery occlusion. Three hours thereafter, mice were intravenously injected with Maclpil siRNA or scramble siRNA nanoparticles. Bone marrow cell-derived macrophages were transfected with Maclpil or scramble siRNA and subjected to oxygen glucose deprivation culture. The influence of silencing Maclpil on stroke outcomes, neuroinflammation, and macrophage fates was assessed via histology, flow cytometry, Western blotting, and quantitative PCR analysis.
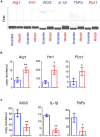
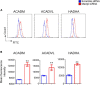
Results: Three days following stroke induction, siRNA silencing Maclpil substantially reduced ischemic infarction size and improved neurological behaviors. Silencing Maclpil also markedly attenuated the accumulation of monocyte-derived macrophages, CD4+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells in the ischemic hemisphere without affecting microglia cellularity. Reciprocally, myeloid cells and both subsets of T cells were elevated in mouse peripheral blood following Maclpil siRNA treatment. Under oxygen glucose deprivation conditions that mimicked hypoxia and hypoglycemia in vitro, Maclpil siRNA silencing augmented macrophage apoptosis in conjunction with upregulation of proapoptotic Bax and caspase 3 expressions. siRNA knocking down Maclpil skewed macrophages from proinflammatory classical toward anti-inflammatory alternative activation as evidenced by increased arginase 1, Ym1, and Fizz1 and reduced inducible nitric oxide synthase, IL-1β, and TNF-α mRNA levels. Consistent with macrophage phenotype switching, silencing Maclpil by siRNA enhanced fatty acid oxidation as indicated by increased mRNA levels of 3 key metabolic enzymes (ACADM, ACADVL, and HADHA).
Conclusion: Systemically silencing Maclpil by siRNA nanoparticles attenuated experimental ischemic stroke by promoting macrophage apoptosis and anti-inflammatory alternative activation. Identifying and targeting Maclpil human homolog(s) may help develop a novel therapy for stroke clinical management.
Keywords: SiRNA nanoparticles; ischemic stroke; lncRNA maclpil; macrophages; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Liu, Chen, Chen, Han, Xue and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
LCP1 knockdown in monocyte-derived macrophages: mitigating ischemic brain injury and shaping immune cell signaling and metabolism.Theranostics. 2024 Jan 1;14(1):159-175. doi: 10.7150/thno.88678. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38164159 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing the lncRNA Maclpil in pro-inflammatory macrophages attenuates acute experimental ischemic stroke via LCP1 in mice.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020 Apr;40(4):747-759. doi: 10.1177/0271678X19836118. Epub 2019 Mar 21. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020. PMID: 30895879 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-19 alleviates brain injury by anti-inflammatory effects in a mice model of focal cerebral ischemia.Brain Res. 2016 Nov 1;1650:172-177. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.09.006. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27608956
-
Sult2b1 deficiency exacerbates ischemic stroke by promoting pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization in mice.Theranostics. 2021 Nov 1;11(20):10074-10090. doi: 10.7150/thno.61646. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34815805 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA Malat1 Regulates Cerebrovascular Pathologies in Ischemic Stroke.J Neurosci. 2017 Feb 15;37(7):1797-1806. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3389-16.2017. Epub 2017 Jan 16. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28093478 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nanomaterial-Based Strategies for Attenuating T-Cell-Mediated Immunodepression in Stroke Patients: Advancing Research Perspectives.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jun 12;19:5793-5812. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S456632. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38882535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Transcriptomic Signatures between Monkeypox-Infected Monkey and Human Cell Lines.J Immunol Res. 2022 Sep 1;2022:3883822. doi: 10.1155/2022/3883822. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36093436 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of Gold Nanoparticles: Impacts on Immune Cells and Mechanisms of Action.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Aug 6;15(15):1201. doi: 10.3390/nano15151201. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40801739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain alarm by self-extracellular nucleic acids: from neuroinflammation to neurodegeneration.J Biomed Sci. 2023 Aug 7;30(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12929-023-00954-y. J Biomed Sci. 2023. PMID: 37550658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LCP1 knockdown in monocyte-derived macrophages: mitigating ischemic brain injury and shaping immune cell signaling and metabolism.Theranostics. 2024 Jan 1;14(1):159-175. doi: 10.7150/thno.88678. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38164159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kleindorfer DO, Towfighi A, Chaturvedi S, Cockroft KM, Gutierrez J, Lombardi-Hill D, et al. 2021 Guideline for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline from the American heart association/American stroke association. Stroke. (2021) 52:e364–467. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

