Latest Advancements on Combating Obesity by Targeting Human Brown/Beige Adipose Tissues
- PMID: 35600577
- PMCID: PMC9114493
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.884944
Latest Advancements on Combating Obesity by Targeting Human Brown/Beige Adipose Tissues
Abstract
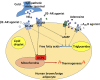
Obesity is defined as overaccumulation of white adipose tissue in the body, mainly under the skin (subcutaneous adiposity) or in the abdominal cavity (visceral adiposity). It could be the origin of various metabolic disorders including hypertension, hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases etc. Active adipose tissue was discovered in humans through 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography coupled with Computer Tomography (18F FDG-PET/CT), which was initially performed for tumor scanning. Since human active adipose tissue is probably composed of brown and beige adipose tissues and they burn white adipose tissue to generate heat, targeting human brown/beige adipose tissue to induce their thermogenic function is considered significant to combat obesity. In this review, we describe the latest advancements on promising therapeutic strategies to combat obesity by targeting human thermogenic adipose tissues to achieve further metabolic balance in humans.
Keywords: beige adipose tissue; brown adipose tissue; human; metabolism; obesity.
Copyright © 2022 Pan and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Petrovic N, Walden TB, Shabalina IG, Timmons JA, Cannon B, Nedergaard J. Chronic Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma (Ppargamma) Activation of Epididymally Derived White Adipocyte Cultures Reveals a Population of Thermogenically Competent, UCP1-containing Adipocytes Molecularly Distinct From Classic Brown Adipocytes. J Biol Chem (2010) 285(10):7153–64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.053942 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

