Thyroid Cancer and COVID-19: Prospects for Therapeutic Approaches and Drug Development
- PMID: 35600591
- PMCID: PMC9114699
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.873027
Thyroid Cancer and COVID-19: Prospects for Therapeutic Approaches and Drug Development
Abstract
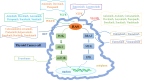
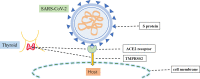
Thyroid cancer is the most prevalent endocrine malignancy and the reported incidence of thyroid cancer has continued to increase in recent years. Since 2019, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been spreading worldwide in a global pandemic. COVID-19 aggravates primary illnesses and affects disease management; relevant changes include delayed diagnosis and treatment. The thyroid is an endocrine organ that is susceptible to autoimmune attack; thus, thyroid cancer after COVID-19 has gradually attracted attention. Whether COVID-19 affects the diagnosis and treatment of thyroid cancer has also attracted the attention of many researchers. This review examines the literature regarding the influence of COVID-19 on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of thyroid cancer; it also focuses on drug therapies to promote research into strategies for improving therapy and management in thyroid cancer patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; drug target; immunotherapy; multikinase inhibitors; thyroid cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Qu, Hui, Shen, Kan, Hou, Sun and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thyroid cancer in the Era of COVID-19.Endocrine. 2020 Oct;70(1):1-5. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02439-6. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Endocrine. 2020. PMID: 32754886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid cancer and COVID-19: experience at one single thyroid disease referral center.Endocrine. 2021 May;72(2):332-339. doi: 10.1007/s12020-021-02650-z. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Endocrine. 2021. PMID: 33638758 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid disease in the time of COVID-19.Endocrine. 2020 Jun;68(3):471-474. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02364-8. Epub 2020 Jun 7. Endocrine. 2020. PMID: 32507963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review.JAMA. 2020 Aug 25;324(8):782-793. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12839. JAMA. 2020. PMID: 32648899 Review.
-
The Role of Chest Radiograph, Procalcitonin and Moxifloxacin in Diagnosis and Management of Breast Cancer Patients with COVID-19.Acta Med Indones. 2020 Apr;52(2):163-171. Acta Med Indones. 2020. PMID: 32778631
Cited by
-
Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for determining neutrophil elastase (NE) - a potential useful marker of multi-organ damage observed in COVID-19 and post-Covid-19 (PCS).Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Feb 25;12:1542898. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1542898. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40070691 Free PMC article.
-
Papillary Thyroid Cancer Trends in the Wake of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Is There a Shift toward a More Aggressive Entity?Diseases. 2024 Mar 20;12(3):62. doi: 10.3390/diseases12030062. Diseases. 2024. PMID: 38534986 Free PMC article.
-
State of Knowledge About Thyroid Cancers in the Era of COVID-19-A Narrative Review.Biomedicines. 2024 Dec 13;12(12):2829. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122829. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: The thyroid and Covid-19, volume II.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 27;14:1331452. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1331452. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38089608 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
No Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Early Mortality for Thyroid Cancer in the US. Comment on Lee et al. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Thyroid Cancer Surgery. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 3579-3590.Curr Oncol. 2024 Oct 17;31(10):6267-6269. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31100466. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39451770 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

