Simvastatin alleviates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and oxidative stress of high glucose-induced lens epithelial cells in vitro by inhibiting RhoA/ROCK signaling
- PMID: 35601076
- PMCID: PMC9117960
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2022.11347
Simvastatin alleviates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and oxidative stress of high glucose-induced lens epithelial cells in vitro by inhibiting RhoA/ROCK signaling
Abstract
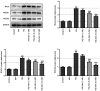
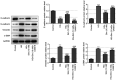
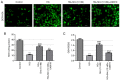
Diabetic cataracts (DC) is one of the main causes of blindness among patients with diabetes mellitus. The aim of the present study was to examine the effect of simvastatin on lens epithelial cells in DC and the underlying mechanism. The viability of SRA01/04 cells treated with different concentrations of simvastatin was detected using a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay before and after high glucose (HG) treatment. The expression levels of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Vimentin and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), proteins associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), in addition to RhoA, Rho-associated kinases (ROCK)1 and ROCK2, proteins related to RhoA/ROCK signaling, were also measured in SRA01/04 cells treated with HG and simvastatin, with or without U46619, using western blot analysis. DCFH-DA dyes, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH)/glutathione disulfide (GSSG) kits were used to measure the levels of oxidative stress parameters in SRA01/04 cells treated with HG and simvastatin with or without U46619. The cell viability of SRA01/04 cells treated with simvastatin was found to be significantly elevated after HG treatment. The protein expression levels of E-cadherin were increased but those of N-cadherin, Vimentin and α-SMA decreased after HG and simvastatin treatment, and this was reversed by U46619. The levels of SOD and GSH-GSSG were found to be increased whereas reactive oxygen species levels were decreased, effects that were reversed by U46619. Additionally, the protein expression levels of RhoA, ROCK1 and ROCK2 were markedly decreased. These findings provided evidence that simvastatin increased HG-induced SRA01/04 cell viability and exerted inhibitory effects on EMT and oxidative stress that occurs during DC.
Keywords: RhoA/Rho-associated protein kinase; diabetic cataract; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; oxidative stress; simvastatin.
Copyright: © Fu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ye W, Ma J, Wang F, Wu T, He M, Li J, Pei R, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhou J. LncRNA MALAT1 regulates miR-144-3p to facilitate epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lens epithelial cells via the ROS/NRF2/Notch1/snail pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020(8184314) doi: 10.1155/2020/8184314. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Panozzo G, Staurenghi G, Dalla Mura G, Giannarelli D, Alessio G, Alongi S, Appolloni R, Baldascino A, Boscia F, Caporossi A, et al. Prevalence of diabetes and diabetic macular edema in patients undergoing senile cataract surgery in Italy: The DIabetes and CATaract study. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2020;30:315–320. doi: 10.1177/1120672119830578. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
