Accuracy of segmented measurement of axial length in ultra-high myopia filled with silicone oil using immersion B-scan ultrasonography
- PMID: 35601170
- PMCID: PMC9091887
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2022.05.16
Accuracy of segmented measurement of axial length in ultra-high myopia filled with silicone oil using immersion B-scan ultrasonography
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the accuracy of segmented measurement of axial length (AL) in high myopia filled with silicone oil by immersion B-scan ultrasonography (immersion B-scan).
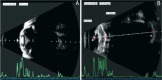
Methods: From June 2016 to June 2020, a total of 67 ultra-high myopia inpatients (67 eyes) who underwent silicone oil removal combined with cataract extraction and intraocular lens (IOL) implantation were retrospectively enrolled. The preoperative axial length (AL) of 31 patients with severe cataract were segmented measured using immersion B-scan (B-scan group) and another 36 patients with mild or moderate cataract were measured using IOLMaster 500 (IOLMaster group). The post-operative ALs in two groups were both measured using IOLMaster 500. The IOL power was calculated with Haigis formula. The differences in ALs between pre- and post-surgery, as well as the postoperative refractive spherical equivalent, absolute refractive error, the prediction deviation of postoperative refraction and best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) were compared.
Results: The pre- and post-operative ALs were 30.46±1.63 mm (range 28.09-33.51 mm) and 30.42±1.70 mm (range 28.03-33.90 mm) in B-scan group (t=0.644, P=0.542) and 30.51±1.21 mm (range 28.03-33.90 mm) and 30.43±1.27mm (range 28.54-33.50 mm) in IOLMaster group (t=1.843, P=0.074), respectively. Three months after surgery, BCVA were 0.45±0.13 (range 0.3-0.9) and 0.44±0.20 (range 0.2-1.0) in B-scan and IOLMaster group respectively (t=0.086, P=0.932). There was no significant difference of the postoperative spherical equivalent (-3.11±0.65 D vs -3.21±0.51 D, t=0.671, P=0.505) and the absolute refractive error (0.589±0.340 vs 0.470±0.245 D, t=1.615, P=0.112) between two groups. In B-scan group, absolute refractive error within ±0.50 D was found in 18 eyes (58.1%), within ±1.00 D in 26 eyes (83.9%), and within ±1.50 D in 31 eyes (100%). In IOLMaster group, absolute refractive error within ±0.50 D was found in 23 eyes (63.9%), within ±1.00 D in 34 eyes (94.4%), and within ±1.50 D in 36 eyes (Z=0.757, P=0.449).
Conclusion: The segmented measurement of ALs by immersion B-scan shows comparable measurement accuracy with that of IOLMaster 500 in ultra-high myopia patients with severe cataract secondary to silicone oil filling and can obtain an ideal postoperative refractive state.
Keywords: IOLMaster; axial length; cataract; high myopia; immersion B-ultrasound; silicone oil.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Accuracy of immersion B-scan ultrasound biometry in high myopic patients with cataract].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Jan;50(1):32-6. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24709131 Chinese.
-
Accuracy of axial length measurements from immersion B-scan ultrasonography in highly myopic eyes.Int J Ophthalmol. 2014 Jun 18;7(3):441-5. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2014.03.10. eCollection 2014. Int J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24967188 Free PMC article.
-
[The analysis of refractive error of long axial high myopic eyes after IOL implantation].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Apr;51(4):276-81. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26081231 Chinese.
-
Accuracy and reliability of IOL master and A-scan immersion biometry in silicone oil-filled eyes.Eye (Lond). 2012 Oct;26(10):1344-8. doi: 10.1038/eye.2012.163. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Eye (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22878446 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative measurements for cataract surgery: a comparison of ultrasound and optical biometric devices.Int Ophthalmol. 2021 Apr;41(4):1521-1530. doi: 10.1007/s10792-021-01714-3. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Int Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33511513
References
-
- Antoun J, Azar G, Jabbour E, Kourie HR, Slim E, Schakal A, Jalkh A. Vitreoretinal surgery with silicone oil tamponade in primary uncomplicated rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: clinical outcomes and complications. Retina. 2016;36(10):1906–1912. - PubMed
-
- Bonfiglio V, Reibaldi M, Macchi I, Fallico M, Pizzo C, Patane C, Russo A, Longo A, Pizzo A, Cillino G, Cillino S, Vadalà M, Rinaldi M, Rejdak R, Nowomiejska K, Toro MD, Avitabile T, Ortisi E. Preoperative, intraoperative and postoperative corticosteroid use as an adjunctive treatment for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. J Clin Med. 2020;9(5):1556. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shu I, Ishikawa H, Nishikawa H, Morikawa S, Okamoto F, Sakamoto T, Sugimoto M, Kondo M, Iwasaki M, Kinoshita T, Toibana T, Mitamura Y, Takamura Y, Motohashi R, Shimura M, Sakurai Y, Takeuchi M, Gomi F. Scleral buckling versus vitrectomy for young Japanese patients with rhegmatogenous retinal detachment in the era of microincision surgery: real-world evidence from a multicentre study in Japan. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019;97(5):e736–e741. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
