Optical Detection of Acetone Using " Turn-Off" Fluorescent Rice Straw Based Cellulose Carbon Dots Imprinted onto Paper Dipstick for Diabetes Monitoring
- PMID: 35601306
- PMCID: PMC9118203
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01492
Optical Detection of Acetone Using " Turn-Off" Fluorescent Rice Straw Based Cellulose Carbon Dots Imprinted onto Paper Dipstick for Diabetes Monitoring
Abstract
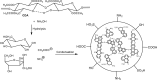
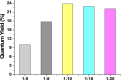
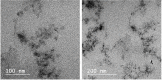
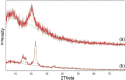
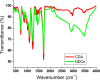
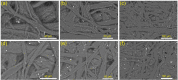
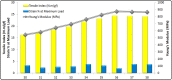
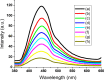
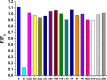
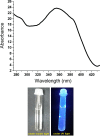
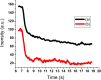
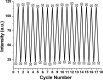
Persistent bad breath has been reported as a sign of serious diabetes health conditions. If an individual's breath has a strong odor of acetone, it may indicate high levels of ketones in the blood owing to diabetic ketoacidosis. Thus, acetone gas in the breath of patients with diabetes can be detected using the current easy-to-use fluorescent test dipstick. In another vein, rice straw waste is the most well-known solid pollutant worldwide. Thus, finding a simple technique to change rice straw into a valuable material is highly important. A straightforward and environmentally friendly approach for reprocessing rice straw as a starting material for the creation of fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots (NCDs) has been established. The preparation process of NCDs was carried out via one-pot hydrothermal carbonization using NH4OH as a passivation substance. A testing strip was developed on the basis of cellulose CD nanoparticles (NPs) immobilized onto cellulose paper assay. The NCDs demonstrated a quantum yield of 23.76%. A fluorescence wavelength was detected at 443 nm upon applying an excitation wavelength of 354 nm. NCDs demonstrated remarkable selectivity for acetone gas as their fluorescence was definitely exposed to quenching by acetone as a consequence of the inner filter effect. A linear correlation was observed across the concentration range of 0.5-150 mM. To detect and measure acetone gas, the present cellulose paper strip has a "switch off" fluorescent signal. A readout limit was accomplished for an aqueous solution of acetone as low as 0.5 mM under ambient conditions. The chromogenic fluorescence of the cellulose assay responsiveness depends on the fluorescence quenching characteristic of the cellulose carbon dots in acetone. A thin fluorescent cellulose carbon dot layer was deposited onto the surface of cellulose strips by a simple impregnation process. CDs were made using NP morphology and analyzed using infrared spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The carbon dot distribution on the paper strip was evaluated by scanning electron microscope and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis. The absorption and fluorescence spectral analyses were investigated. The paper sheets' mechanical qualities were also examined.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preparation of carbon dots-embedded fluorescent carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel for anticounterfeiting applications.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 May 31;238:124028. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124028. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 36924871
-
Preparation of carbon dots from waste cellulose diacetate as a sensor for tetracycline detection and fluorescence ink.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Dec 1;164:4289-4298. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.243. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32891644
-
Optical Recognition of Ammonia and Amine Vapor Using "Turn-on" Fluorescent Chitosan Nanoparticles Imprinted on Cellulose Strips.J Fluoresc. 2019 May;29(3):693-702. doi: 10.1007/s10895-019-02381-5. Epub 2019 Apr 30. J Fluoresc. 2019. PMID: 31041695
-
Fluorescent N/Al Co-Doped Carbon Dots from Cellulose Biomass for Sensitive Detection of Manganese (VII).J Fluoresc. 2019 Nov;29(6):1291-1300. doi: 10.1007/s10895-019-02452-7. Epub 2019 Nov 9. J Fluoresc. 2019. PMID: 31707509
-
Hydrothermal synthesis of green fluorescent nitrogen doped carbon dots for the detection of nitrite and multicolor cellular imaging.Anal Chim Acta. 2019 Dec 20;1090:133-142. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.09.015. Epub 2019 Sep 7. Anal Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31655638
Cited by
-
A solid state electrolyte based enzymatic acetone sensor.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 4;14(1):15461. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66498-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38965300 Free PMC article.
-
Cellulose as Source and Matrix for Fluorescent Chemo-Sensors.J Fluoresc. 2025 Feb 24. doi: 10.1007/s10895-025-04200-6. Online ahead of print. J Fluoresc. 2025. PMID: 39992320 Review.
-
Electrospun Fibrous Nanocomposite Sensing Materials for Monitoring Biomarkers in Exhaled Breath.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Apr 10;15(8):1833. doi: 10.3390/polym15081833. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111980 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoelectronic Detection of Acetone with MIL-53(Al)-NH2 Metal-Organic Framework on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Dec 4;16(48):66377-66386. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c16016. Epub 2024 Nov 21. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39570752 Free PMC article.
-
Capped ZnO quantum dots with a tunable photoluminescence for acetone detection.RSC Adv. 2023 Jun 1;13(24):16453-16470. doi: 10.1039/d3ra00491k. eCollection 2023 May 30. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37274405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . WHO | diabetes fact sheet; WHO, World Health Organization, 2021. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/.
-
- Hijazi M.; Rieu M.; Stambouli V.; Tournier G.; Viricelle J. P.; Pijolat C. Ambient temperature selective ammonia gas sensor based on SnO2-APTES modifications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 440–447. 10.1016/j.snb.2017.10.036. - DOI
-
- Evans G. P.; Powell M. J.; Johnson I. D.; Howard D. P.; Bauer D.; Darr J. A.; Parkin I. P. Room temperature vanadium dioxide-carbon nanotube gas sensors made via continuous hydrothermal flow synthesis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 1119–1129. 10.1016/j.snb.2017.07.152. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

