Flexor Tenosynovitis Caused by Mycobacterium heraklionense
- PMID: 35601512
- PMCID: PMC9120779
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhsg.2021.12.010
Flexor Tenosynovitis Caused by Mycobacterium heraklionense
Abstract
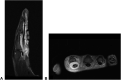
Mycobacterium heraklionense is a rare etiology of serious hand infection with only 2 cases having been reported in literature to date to our knowledge. We describe the case of a 58-year-old woman with persistent swelling and stiffness in her right index finger. Advanced imaging studies in addition to serial surgical debridement with tissue cultures helped to confirm the diagnosis of flexor tenosynovitis caused by M. heraklionense. In this case report, we highlight the clinical evaluation, operative treatment, and antimicrobial therapy leading to the successful care of this disease presentation. Due to its rarity and potential to cause substantial hand infection, M. heraklionense should be included in the differential diagnosis as the cause for chronic flexor tenosynovitis to appropriately minimize morbidity.
Keywords: Flexor tenosynovitis; Mycobacterium heraklionense; Tendon sheath infection.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium heraklionense: An emerging cause of hand tenosynovitis.J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2024 Sep 27;37:100479. doi: 10.1016/j.jctube.2024.100479. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2024. PMID: 39391018 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic tenosynovitis of the hand caused by Mycobacterium heraklionense.Int J Mycobacteriol. 2016 Sep;5(3):273-275. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmyco.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27847009
-
Purulent Flexor Tendon Rupture of the Hand due to Mycobacterium abscessus Infection: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.J Nippon Med Sch. 2022;89(3):347-354. doi: 10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2022_89-110. J Nippon Med Sch. 2022. PMID: 35768271 Review.
-
Mycobacterium heraklionense sp. nov.: A case series.Exp Ther Med. 2015 Oct;10(4):1401-1403. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2683. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26622497 Free PMC article.
-
Flexor Tenosynovitis Caused by Mycobacterium arupense: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.JBJS Case Connect. 2020 Jul-Sep;10(3):e20.00033. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.CC.20.00033. JBJS Case Connect. 2020. PMID: 32910569 Review.
Cited by
-
Mycobacterium heraklionense: An emerging cause of hand tenosynovitis.J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2024 Sep 27;37:100479. doi: 10.1016/j.jctube.2024.100479. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2024. PMID: 39391018 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tortoli E., Gitti Z., Klenk H.P., et al. Survey of 150 strains belonging to the Mycobacterium terrae complex and description of Mycobacterium engbaekii sp. nov., Mycobacterium heraklionense sp. nov. and Mycobacterium longobardum sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2013;63:401–411. - PubMed
-
- Abedalthagafi M., Rosenberg O., Miller S. First report of tenosynovitis in an immunocompetent person caused by Mycobacterium heraklionense. JMM Case Reports. 2014;1:2071.
-
- Aburjania N., Hammert W.C., Bansal M., Boyce B.F., Munsiff S.S. Chronic tenosynovitis of the hand caused by Mycobacterium heraklionense. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2016;5:273–275. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

