c-JUN inhibits mTORC2 and glucose uptake to promote self-renewal and obesity
- PMID: 35601917
- PMCID: PMC9121277
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104325
c-JUN inhibits mTORC2 and glucose uptake to promote self-renewal and obesity
Retraction in
-
Retraction Notice to: c-JUN inhibits mTORC2 and glucose uptake to promote self-renewal and obesity.iScience. 2025 Mar 19;28(4):112231. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112231. eCollection 2025 Apr 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40171491 Free PMC article.
Abstract
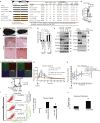
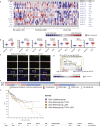
Metabolic syndrome is associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and the risk of cancer. We tested whether oncogenic transcription factor c-JUN metabolically reprogrammed cells to induce obesity and cancer by reduction of glucose uptake, with promotion of the stemness phenotype leading to malignant transformation. Liquid alcohol, high-cholesterol, fat diet (HCFD), and isocaloric dextrin were fed to wild-type or experimental mice for 12 months to promote hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We demonstrated 40% of mice developed liver tumors after chronic HCFD feeding. Disruption of liver-specific c-Jun reduced tumor incidence 4-fold and improved insulin sensitivity. Overexpression of c-JUN downregulated RICTOR transcription, leading to inhibition of the mTORC2/AKT and glycolysis pathways. c-JUN inhibited GLUT1, 2, and 3 transactivation to suppress glucose uptake. Silencing of RICTOR or c-JUN overexpression promoted self-renewal ability. Taken together, c-JUN inhibited mTORC2 via RICTOR downregulation and inhibited glucose uptake via downregulation of glucose intake, leading to self-renewal and obesity.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Cancer; Cell biology; Diabetology; Endocrinology; Molecular biology.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Chen C.L., Uthaya Kumar D.B., Punj V., Xu J., Sher L., Tahara S.M., Hess S., Machida K. NANOG metabolically reprograms tumor-initiating stem-like cells through tumorigenic changes in oxidative phosphorylation and fatty acid metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016;23:206–219. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.12.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

