Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors in the United States (2014-2018): A summary of the CBTRUS statistical report for clinicians
- PMID: 35601966
- PMCID: PMC9113389
- DOI: 10.1093/nop/npac015
Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors in the United States (2014-2018): A summary of the CBTRUS statistical report for clinicians
Abstract
Background: The Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States (CBTRUS) contains information on all primary brain and other central nervous system (CNS) tumors diagnosed in the United States (US). Here we summarize the 2021 CBTRUS annual statistical report for clinicians.
Methods: Incidence survival data are obtained from the Centers for Disease Control's National Program of Cancer Registries (NPCR) and National Cancer Institute's Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program. Survival data are obtained from NPCR. Mortality data are obtained from the National Vital Statistics System. Incidence and mortality rates are age-adjusted using the 2000 US population and presented per 100,000 population.
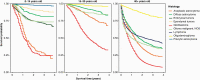
Results: An annual average of 86,355 cases of primary malignant and nonmalignant CNS tumors were diagnosed over the period 2014-2018, corresponding to an average annual age-adjusted incidence rate of 24.25. The most commonly occurring malignant tumor was glioblastoma (14.3%), and the most common predominately nonmalignant tumor was meningioma (39%). Over the 2014-2018 period, there were 16,606 annual average deaths due to malignant primary CNS tumors, corresponding to an average annual age-adjusted mortality rate of 4.43. In this report we detail key incidence, survival, and mortality statistics for major primary CNS tumor histologies, highlighting relevant differences by age, sex, and race.
Conclusions: This summary describes the most up to date population-based incidence of primary malignant and nonmalignant brain and other CNS tumors in the US, and mortality and survival for primary malignant tumors and aims to serve as a useful resource for clinicians.
Keywords: CBTRUS; CNS tumors; brain tumors; epidemiology; incidence; mortality; neuro-oncology; survival.
Published by Oxford University Press 2022.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). National Program of Cancer Registries Cancer Surveillance System Rationale and Approach. 1999; http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/npcr/pdf/npcr_css.pdf. Accessed July 21, 2020.
-
- Cancer Registries Amendment Act, 102nd Cong. § 515. 1992; https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/STATUTE-106/pdf/STATUTE-106-Pg3372.pdf
-
- Benign Brain Tumor Cancer Registries Amendment Act, 107th Cong. § 260. 2002; http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/PLAW-107publ260/pdf/PLAW-107publ260.pdf. Accessed July 21, 2020.

