Phlorotannins-bioactivity and extraction perspectives
- PMID: 35601997
- PMCID: PMC9112266
- DOI: 10.1007/s10811-022-02749-4
Phlorotannins-bioactivity and extraction perspectives
Abstract
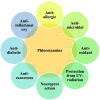
Phlorotannins, a seaweed based class of polyphenolic compounds, have proven to possess potential bioactivities such as antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-allergic, anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancerous, neuroprotection etc. These bioactivities have further increased demand globally and sustainable techniques such as supercritical fluid extraction, microwave assisted extraction, enzyme assisted extraction, extraction using deep eutectic solvents etc. are being explored currently for production of phlorotannin-rich extracts. In spite of such well documented bioactivities, very few phlorotannin-based nutraceuticals are available commercially which highlights the significance of generating consumer awareness about their physiological benefits. However, for industry level commercialization accurate quantification of phlorotannins with respect to the different classes is vital requiring sophisticated analytical techniques such as mass spectrometry, 1H-NMR spectroscopy etc. owing to the wide structural diversity. This review summarizes the extraction and bioactivities of phlorotannins based on the findings of in vivo and in vitro studies.
Keywords: Anti-proliferative; Anti-viral; Histamine; Hyaluronidase; Lipopolysaccharide; Melanosis; Neurodegeneration; Nitric oxide; Phloroethols; Supercritical fluid extraction.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Abdelhamid A, Lajili S, Elkaibi MA, Ben Salem Y, Abdelhamid A, Muller CD, Majdoub H, Kraiem J, Bouraoui A. Optimized extraction, preliminary characterization and evaluation of the in vitro anticancer activity of phlorotannin-rich fraction from the brown seaweed, Cystoseira sedoides. J Aquat Food Prod Technol. 2019;28:892–909. doi: 10.1080/10498850.2019.1662865. - DOI
-
- Ahn G, Amagai Y, Matsuda A, Kang SM, Lee W, Jung K, Oida K, Jang H, Ishizaka S, Matsuda K, Jeon YJ, Jee Y, Matsuda H, Tanaka A. Dieckol, a phlorotannin of Ecklonia cava, suppresses IgE-mediated mast cell activation and passive cutaneous anaphylactic reaction. Exp Dermatol. 2015;24:968–970. doi: 10.1111/exd.12814. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arunkumar K, Raj R, Raja R, Carvalho IS. Brown seaweeds as a source of anti-hyaluronidase compounds. S Afr J Bot. 2021;139:470–477. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2021.03.036. - DOI
-
- Balboa EM, Cond E, Moure A, Falqué E, Domínguez H (2013) In vitro antioxidant properties of crude extracts and compounds from brown algae. Food Chem 138:1764–1785 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources