Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Strategically Combined With Origanum vulgare Derivatives: Antibacterial Mechanism of Action and Effect on Multidrug-Resistant Strains
- PMID: 35602016
- PMCID: PMC9121793
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.842600
Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Strategically Combined With Origanum vulgare Derivatives: Antibacterial Mechanism of Action and Effect on Multidrug-Resistant Strains
Abstract
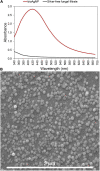
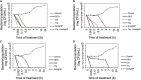
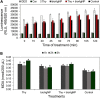
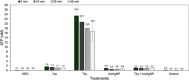
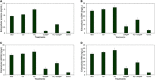
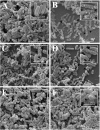
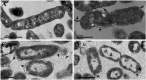
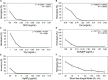
Multidrug-resistant bacteria have become a public health problem worldwide, reducing treatment options against several pathogens. If we do not act against this problem, it is estimated that by 2050 superbugs will kill more people than the current COVID-19 pandemic. Among solutions to combat antibacterial resistance, there is increasing demand for new antimicrobials. The antibacterial activity of binary combinations containing bioAgNP (biogenically synthesized silver nanoparticles using Fusarium oxysporum), oregano essential oil (OEO), carvacrol (Car), and thymol (Thy) was evaluated: OEO plus bioAgNP, Car plus bioAgNP, Thy plus bioAgNP, and Car plus Thy. This study shows that the mechanism of action of Thy, bioAgNP, and Thy plus bioAgNP involves damaging the membrane and cell wall (surface blebbing and disruption seen with an electron microscope), causing cytoplasmic molecule leakage (ATP, DNA, RNA, and total proteins) and oxidative stress by enhancing intracellular reactive oxygen species and lipid peroxidation; a similar mechanism happens for OEO and Car, except for oxidative stress. The combination containing bioAgNP and oregano derivatives, especially thymol, shows strategic antibacterial mechanism; thymol disturbs the selective permeability of the cell membrane and consequently facilitates access of the nanoparticles to bacterial cytoplasm. BioAgNP-treated Escherichia coli developed resistance to nanosilver after 12 days of daily exposition. The combination of Thy and bioAgNP prevented the emergence of resistance to both antimicrobials; therefore, mixture of antimicrobials is a strategy to extend their life. For antimicrobials alone, minimal bactericidal concentration ranges were 0.3-2.38 mg/ml (OEO), 0.31-1.22 mg/ml (Car), 0.25-1 mg/ml (Thy), and 15.75-31.5 μg/ml (bioAgNP). The time-kill assays showed that the oregano derivatives acted very fast (at least 10 s), while the bioAgNP took at least 30 min to kill Gram-negative bacteria and 7 h to kill methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). All the combinations resulted in additive antibacterial effect, reducing significantly minimal inhibitory concentration and acting faster than the bioAgNP alone; they also showed no cytotoxicity. This study describes for the first time the effect of Car and Thy combined with bioAgNP (produced with F. oxysporum components) against bacteria for which efficient antimicrobials are urgently needed, such as carbapenem-resistant strains (E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and MRSA.
Keywords: ESKAPEE pathogens; Fusarium oxysporum; MRSA; carbapenem resistance; carvacrol; green nanotechnology; oregano oil; thymol.
Copyright © 2022 Scandorieiro, Rodrigues, Nishio, Panagio, de Oliveira, Durán, Nakazato and Kobayashi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibiofilm Effect of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Combined with Oregano Derivatives against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Apr 14;12(4):756. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12040756. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107119 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic and Additive Effect of Oregano Essential Oil and Biological Silver Nanoparticles against Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains.Front Microbiol. 2016 May 23;7:760. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00760. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27242772 Free PMC article.
-
Origanum vulgare essential oil: antibacterial activities and synergistic effect with polymyxin B against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Dec;47(12):9615-9625. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05989-0. Epub 2020 Nov 15. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33190200
-
Sulopenem: An Intravenous and Oral Penem for the Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections Due to Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria.Drugs. 2022 Apr;82(5):533-557. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01688-1. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35294769 Review.
-
Cefiderocol: A Siderophore Cephalosporin with Activity Against Carbapenem-Resistant and Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli.Drugs. 2019 Feb;79(3):271-289. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1055-2. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30712199 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic Antimicrobial Activity of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles and Acanthospermum australe Essential Oil against Skin Infection Pathogens.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 20;13(7):674. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070674. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061356 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles on the Quorum-Sensing System of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and PA14.Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 30;10(9):1755. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10091755. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36144357 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogel Containing Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles and Origanum vulgare Essential Oil for Burn Wounds: Antimicrobial Efficacy Using Ex Vivo and In Vivo Methods Against Multidrug-Resistant Microorganisms.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 10;17(4):503. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040503. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284498 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenic silver nanoparticles and cinnamaldehyde as an effective sanitizer for fresh sweet grape tomatoes.J Food Sci Technol. 2023 Sep;60(9):2477-2485. doi: 10.1007/s13197-023-05770-8. Epub 2023 May 30. J Food Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37424585 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing the global challenge of bacterial drug resistance: insights, strategies, and future directions.Front Microbiol. 2025 Feb 24;16:1517772. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1517772. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40066274 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agnihotri S., Mukherji S., Mukherji S. (2014). Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5-100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv. 4 3974–3983. 10.1039/c3ra44507k - DOI
-
- Alvarez M. V., Ortega-Ramirez L. A., Gutierrez-Pacheco M. M., Bernal-Mercado A. T., Rodriguez-Garcia I., Gonzalez-Aguilar G. A., et al. (2014). Oregano essential oil-pectin edible films as anti-quorum sensing and food antimicrobial agents. Front. Microbiol. 5:699. 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00699 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrade P. F., Nakazato G., Durán N. (2017). Additive interaction of carbon dots extracted from soluble coffee and biogenic silver nanoparticles against bacteria. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 838:012028. 10.1088/1742-6596/838/1/012028 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

