Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities of Chlorogenic Acid Against Yersinia enterocolitica
- PMID: 35602020
- PMCID: PMC9117966
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.885092
Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities of Chlorogenic Acid Against Yersinia enterocolitica
Abstract
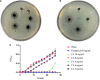
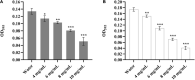
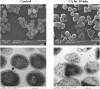
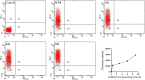
Nowadays, developing new and natural compounds with antibacterial activities from plants has become a promising approach to solve antibiotic resistance of pathogenic bacteria. Chlorogenic acid (CA), as a kind of phenolic acid existing in many plants, has been found to process multifunctional activities including antibacterial activity. Herein, the antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of CA against Yersinia enterocolitica (Y. enterocolitica) were tested for the first time, and its mechanism of action was investigated. It was demonstrated that CA could exert outstanding antibacterial activity against Y. enterocolitica. Biofilm susceptibility assays further indicated that CA could inhibit biofilm formation and decrease the established biofilm biomass of Y. enterocolitica. It was deduced that through binding to Y. enterocolitica, CA destroyed the cell membrane, increased the membrane permeability, and led to bacterial cell damage. In addition, the transcriptomic analysis revealed that CA could disorder many physiological pathways, mainly including the ones of antagonizing biofilms and increasing cell membrane permeability. Finally, the spiked assay showed that the growth of Y. enterocolitica in milk was significantly inhibited by CA. Taken together, CA, as an effective bactericidal effector with application potential, exerts antagonistic activity against Y. enterocolitica by mainly intervening biofilm formation and membrane permeability-related physiological pathways.
Keywords: Yersinia enterocolitica; antibacterial activity; antibiofilm activity; antibiotic resistance; chlorogenic acid.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Peng, Chi, Yu, Yang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
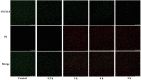

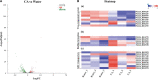
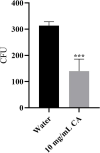

References
-
- Alsolmei F. A., Li H., Pereira S. L., Krishnan P., Johns P. W., Siddiqui R. A. (2019). Polyphenol-enriched plum extract enhances myotubule formation and anabolism while attenuating colon cancer-induced cellular damage in C2C12 cells. Nutrients 11:1077. Epub 2019/05/18. PubMed ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC6566394 10.3390/nu11051077 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bottone E. J. (2015). Yersinia enterocolitica: revisitation of an enduring human pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Newslett. 37 1–8. 10.1016/j.clinmicnews.2014.12.003 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

