Preliminary Study on the Combination Effect of Clindamycin and Low Dose Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole on Severe Pneumocystis Pneumonia After Renal Transplantation
- PMID: 35602475
- PMCID: PMC9120531
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.827850
Preliminary Study on the Combination Effect of Clindamycin and Low Dose Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole on Severe Pneumocystis Pneumonia After Renal Transplantation
Abstract
Objective: Evaluate the effect of the combination of clindamycin with low-dose trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) regimen on sever Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) after renal transplantation.
Method: 20 severe PCP patients after renal transplantation were included in this historical-control, retrospective study. A 10 patients were treated with the standard dose of TMP/SMX (T group), the other 10 patients were treated with the combination of clindamycin and low dose TMP/SMX (CT group).
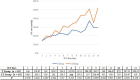
Results: Although there was no significant difference in the hospital survival between the two groups, the CT protocol improved the PaO2/FiO2 ratio more significantly and rapidly after the 6th ICU day (1.51 vs. 0.38, P = 0.014). CT protocol also ameliorated the pulmonary infiltration and the lactate dehydrogenase level more effectively. Moreover, the CT protocol reduced the incidence of pneumomediastinum (0 vs. 50%, P = 0.008), the length of hospital staying (26.5 vs. 39.0 days, P = 0.011) and ICU staying (12.5 vs. 22.5 days, P = 0.008). Furthermore, more thrombocytopenia (9/10 vs. 3/10, P = 0.020) was emerged in the T group than in the CT group. The total adverse reaction rate was much lower in the CT group than in the T group (8/80 vs. 27/80, P < 0.001). Consequently, the dosage of TMP/SMX was reduced in 8 patients, while only 2 patients in the CT group received TMP/SMX decrement (P = 0.023).
Conclusion: The current study proposed that clindamycin combined with low-dose TMP/SMX was more effective and safer the than single use of TMP/SMX for severe PCP patients after renal transplantation (NCT04328688).
Keywords: Pneumocystis pneumonia; clindamycin; combination; renal transplantation; trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.
Copyright © 2022 Gu, Liu, Huang, Liu, He, Yang, Liu, Xu, Rong, Zhu, Luo and Ju.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bollee G, Sarfati C, Thiery G, Bergeron A, de Miranda S, Menotti J, et al. Clinical picture of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in cancer patients. Chest. (2007) 132:1305–10. - PubMed
-
- Roblot F, Godet C, Le Moal G, Garo B, Faouzi Souala M, Dary M, et al. Analysis of underlying diseases and prognosis factors associated with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in immunocompromised HIV-negative patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. (2002) 21:523–31. 10.1007/s10096-002-0758-5 - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

