The E-Id Axis Instructs Adaptive Versus Innate Lineage Cell Fate Choice and Instructs Regulatory T Cell Differentiation
- PMID: 35603170
- PMCID: PMC9120639
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.890056
The E-Id Axis Instructs Adaptive Versus Innate Lineage Cell Fate Choice and Instructs Regulatory T Cell Differentiation
Abstract
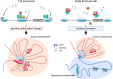
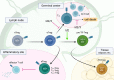
Immune responses are primarily mediated by adaptive and innate immune cells. Adaptive immune cells, such as T and B cells, evoke antigen-specific responses through the recognition of specific antigens. This antigen-specific recognition relies on the V(D)J recombination of immunoglobulin (Ig) and T cell receptor (TCR) genes mediated by recombination-activating gene (Rag)1 and Rag2 (Rag1/2). In addition, T and B cells employ cell type-specific developmental pathways during their activation processes, and the regulation of these processes is strictly regulated by the transcription factor network. Among these factors, members of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor mammalian E protein family, including E12, E47, E2-2, and HEB, orchestrate multiple adaptive immune cell development, while their antagonists, Id proteins (Id1-4), function as negative regulators. It is well established that a majority of T and B cell developmental trajectories are regulated by the transcriptional balance between E and Id proteins (the E-Id axis). E2A is critically required not only for B cell but also for T cell lineage commitment, whereas Id2 and Id3 enforce the maintenance of naïve T cells and naïve regulatory T (Treg) cells. Here, we review the current knowledge of E- and Id-protein function in T cell lineage commitment and Treg cell differentiation.
Keywords: E-Id axis; Rag gene expression; T cell versus ILCs; T-lineage commitment; Treg differentiation.
Copyright © 2022 Hidaka, Miyazaki and Miyazaki.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Evolution of Rag Gene Enhancers and Transcription Factor E and Id Proteins in the Adaptive Immune System.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 31;22(11):5888. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115888. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34072618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The E-Id Protein Axis Specifies Adaptive Lymphoid Cell Identity and Suppresses Thymic Innate Lymphoid Cell Development.Immunity. 2017 May 16;46(5):818-834.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.04.022. Immunity. 2017. PMID: 28514688 Free PMC article.
-
The E-Id axis specifies adaptive and innate lymphoid lineage cell fates.J Biochem. 2022 Oct 19;172(5):259-264. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvac068. J Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36000775 Review.
-
Helix-Loop-Helix Proteins in Adaptive Immune Development.Front Immunol. 2022 May 12;13:881656. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.881656. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35634342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hormonal regulation and differential actions of the helix-loop-helix transcriptional inhibitors of differentiation (Id1, Id2, Id3, and Id4) in Sertoli cells.Endocrinology. 2001 May;142(5):1727-36. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.5.8134. Endocrinology. 2001. PMID: 11316735
Cited by
-
Covalent Dynamic DNA Networks to Translate Multiple Inputs into Programmable Outputs.J Am Chem Soc. 2025 Feb 19;147(7):5755-5763. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c13854. Epub 2025 Feb 5. J Am Chem Soc. 2025. PMID: 39905964 Free PMC article.
-
A feedback amplifier circuit with Notch and E2A orchestrates T-cell fate and suppresses the innate lymphoid cell lineages during thymic ontogeny.Genes Dev. 2025 Mar 3;39(5-6):384-400. doi: 10.1101/gad.352111.124. Genes Dev. 2025. PMID: 39904558 Free PMC article.
-
Contextual computation by competitive protein dimerization networks.Cell. 2025 Apr 3;188(7):1984-2002.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.01.036. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Cell. 2025. PMID: 39978343 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Tubulin Enhances CXCR4 Transcription and Promotes Chemotaxis Through TCF12 Transcription Factor in human Hematopoietic Stem Cells.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 Jul;19(5):1328-1339. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10543-z. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 37067645
-
Transcription factor 4 is a key mediator of oncogenesis in neuroblastoma by promoting MYC activity.Mol Oncol. 2025 Mar;19(3):808-824. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13714. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Mol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39119816 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

