SARS-CoV-2 introductions and early dynamics of the epidemic in Portugal
- PMID: 35603268
- PMCID: PMC9053228
- DOI: 10.1038/s43856-022-00072-0
SARS-CoV-2 introductions and early dynamics of the epidemic in Portugal
Abstract
Background: Genomic surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in Portugal was rapidly implemented by the National Institute of Health in the early stages of the COVID-19 epidemic, in collaboration with more than 50 laboratories distributed nationwide.
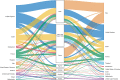
Methods: By applying recent phylodynamic models that allow integration of individual-based travel history, we reconstructed and characterized the spatio-temporal dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 introductions and early dissemination in Portugal.
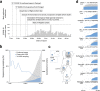
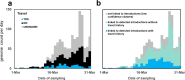
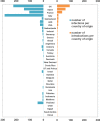
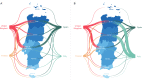
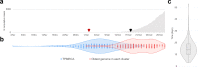
Results: We detected at least 277 independent SARS-CoV-2 introductions, mostly from European countries (namely the United Kingdom, Spain, France, Italy, and Switzerland), which were consistent with the countries with the highest connectivity with Portugal. Although most introductions were estimated to have occurred during early March 2020, it is likely that SARS-CoV-2 was silently circulating in Portugal throughout February, before the first cases were confirmed.
Conclusions: Here we conclude that the earlier implementation of measures could have minimized the number of introductions and subsequent virus expansion in Portugal. This study lays the foundation for genomic epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 in Portugal, and highlights the need for systematic and geographically-representative genomic surveillance.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; Viral infection.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Weekly operational update on COVID-19https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/weekly-updates/wou_... (2021).
-
- Dong, E., Du, H. & Gardner, L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet Infect Dis. 20, 533–534 (2020). Erratum in: Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Sep;e215. PMID: 32087114; PMCID: PMC7159018. https://www.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594740fd4029942.... - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

