A 2-month field cohort study of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva of BNT162b2 vaccinated nursing home workers
- PMID: 35603280
- PMCID: PMC9053279
- DOI: 10.1038/s43856-021-00067-3
A 2-month field cohort study of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva of BNT162b2 vaccinated nursing home workers
Abstract
Background: Nursing home (NH) residents have been severely affected during the COVID-19 pandemic because of their age and underlying comorbidities. Infection and outbreaks in NHs are most likely triggered by infected workers. Screening for asymptomatic NH workers can prevent risky contact and viral transmission to the residents. This study examined the effect of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID‑19 (Comirnaty®; BioNTech and Pfizer) vaccination on the saliva excretion of SARS-CoV-2 among NH workers, through weekly saliva RT-qPCR testing.
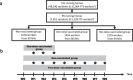
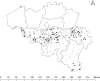
Methods: A 2-month cohort study was conducted among 99 NHs in the Walloon region (Belgium), at the start of February 2021. Three groups of workers, i.e., non-vaccinated (n = 1618), one-dosed vaccinated (n = 1454), and two-dosed vaccinated (n = 2379) of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID‑19 vaccine, were followed-up weekly. Their saliva samples were used to monitor the shedding of SARS-CoV-2. All positive samples were sequenced and genotyped to identify the circulating wild-type virus or variants of concern.
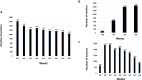
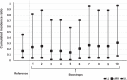
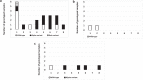
Results: The protection fraction against the excretion of the SARS-CoV-2 in the saliva samples of the workers after the second dose is estimated at 0.90 (95% CI: 0.18; 0.99) at 1 week and 0.83 (95% CI: 0.54; 0.95) at 8 weeks. We observe more circulating SARS-CoV-2 and a greater variability of viral loads in the unvaccinated group compared to those of the vaccinated group.
Conclusions: This field cohort study advances our knowledge of the efficacy of the mRNA BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine on the viral shedding in the saliva specimens of vaccinated NH workers, contributing to better decision-making in public health interventions and management.
Keywords: Epidemiology; RNA vaccines.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsF.B. and L.G. are the inventors of the device used in the saliva collection kit. This device was patented (EP20186086.3) and produced by Diagenode (Seraing, Belgium) under a commercial agreement with the University of Liège. This does not alter the adherence to all journal policies on sharing data and materials, as detailed online in the Author Guide. All other authors do not have competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

