Effects of Long-term Metformin and Lifestyle Interventions on Cardiovascular Events in the Diabetes Prevention Program and Its Outcome Study
- PMID: 35603600
- PMCID: PMC9179081
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056756
Effects of Long-term Metformin and Lifestyle Interventions on Cardiovascular Events in the Diabetes Prevention Program and Its Outcome Study
Abstract
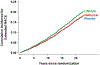
Background: Lifestyle intervention and metformin have been shown to prevent diabetes; however, their efficacy in preventing cardiovascular disease associated with the development of diabetes is unclear. We examined whether these interventions reduced the incidence of major cardiovascular events over a 21-year median follow-up of participants in the DPP trial (Diabetes Prevention Program) and DPPOS (Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study).
Methods: During DPP, 3234 participants with impaired glucose tolerance were randomly assigned to metformin 850 mg twice daily, intensive lifestyle or placebo, and followed for 3 years. During the next 18-year average follow-up in DPPOS, all participants were offered a less intensive group lifestyle intervention, and unmasked metformin was continued in the metformin group. The primary outcome was the first occurrence of nonfatal myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular death adjudicated by standard criteria. An extended cardiovascular outcome included the primary outcome or hospitalization for heart failure or unstable angina, coronary or peripheral revascularization, coronary heart disease diagnosed by angiography, or silent myocardial infarction by ECG. ECGs and cardiovascular risk factors were measured annually.
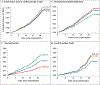
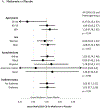
Results: Neither metformin nor lifestyle intervention reduced the primary outcome: metformin versus placebo hazard ratio 1.03 (95% CI, 0.78-1.37; P = 0.81) and lifestyle versus placebo hazard ratio 1.14 (95% CI, 0.87-1.50; P = 0.34). Risk factor adjustment did not change these results. No effect of either intervention was seen on the extended cardiovascular outcome.
Conclusions: Neither metformin nor lifestyle reduced major cardiovascular events in DPPOS over 21 years despite long-term prevention of diabetes. Provision of group lifestyle intervention to all, extensive out-of-study use of statin and antihypertensive agents, and reduction in the use of study metformin together with out-of-study metformin use over time may have diluted the effects of the interventions.
Registration: URL: https://www.
Clinicaltrials: gov; Unique identifiers: DPP (NCT00004992) and DPPOS (NCT00038727).
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; diabetes mellitus, type 2; metformin.
Figures
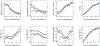

Comment in
-
Shouldn't Preventing Type 2 Diabetes Also Prevent Its Long-Term Consequences?Circulation. 2022 May 31;145(22):1642-1644. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.060026. Epub 2022 May 31. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 35639853 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barrett-Connor E, Wingard D, Wong N, Goldberg R. Diabetes and Heart Disease. In: Cowie CC, Casagrande SS, Menke A, Cissell MA, Eberhardt MS, Meigs JB, Gregg EW, Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Becker DJ, et al. , editors. Diabetes in America, 3rd ed. Bethesda, (MD), National Institutes of Health (US); 2018. Aug. CHAPTER 18.
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998;352:837–853. - PubMed
-
- The Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group. Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC Jr, Bigger JT, Buse JB, Cushman WC, Genuth S, Ismail-Beigi F, Grimm RH Jr, et al. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2545–2559. Doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0802743. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 DK048412/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048375/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048468/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048387/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048377/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048407/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048437/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048406/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048397/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK111022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048339/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048514/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048485/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048411/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048443/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048380/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048400/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048489/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048349/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States

