Clinical Efficacy of Soluble Thrombomodulin, Tissue Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor complex, Thrombin-Antithrombin complex,α2-Plasmininhibitor-Plasmin complex in Pediatric Sepsis
- PMID: 35603624
- PMCID: PMC9134456
- DOI: 10.1177/10760296221102929
Clinical Efficacy of Soluble Thrombomodulin, Tissue Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor complex, Thrombin-Antithrombin complex,α2-Plasmininhibitor-Plasmin complex in Pediatric Sepsis
Abstract
Objective: To investigated the clinical efficacy of Soluble thrombomodulin (sTM), tissue plasminogen activator inhibitor complex (t-PAI·C),thrombin-antithrombin complex (TAT),α2-plasmininhibitor-plasmin complex (PIC) in pediatric sepsis and pediatrics sepsis-induced coagulopathy (pSIC).
Methods: We prospectively collected patient data with sepsis diagnosed in the PICU of Shanghai Children's Medical Center from June 2019 to June 2021. sTM,t-PAI·C, TAT,PIC and classical coagulation laboratory tests (CCTs) were evaluated on the day of sepsis diagnosis.
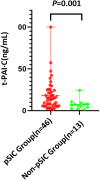
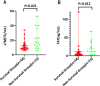
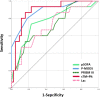
Results: Fifty-nine children were enrolled, There were significant differences in t-PAI·C (P = 0.001), Plt (P < 0.001), PT (P < 0.001), INR (P < 0.001), aPTT (P < 0.001), and TT (P = 0.048) between the pSIC and non-pSIC groups, logistic regression analysis showed that Plt (P = 0.032) was an independent risk factor for pSIC. Logistic regression analysis showed that sTM (P = 0.007) and Plt (P = 0.016) were independent risk factors for the outcome in pediatrics sepsis following discharge. The AUC of sTM combined with Plt on the mortality outcome of children with sepsis at discharge was 0.889 (95%CI: 0.781,0.956). which was better than that for PRISM III (AUC, 0.723), pSOFA (AUC, 0.764), and blood Lac (AUC, 0.717) when sepsis was diagnosed in the PICU.
Conclusions: The t-PAI·C increased in children with pSIC. The prediction of sepsis outcome using sTM combined with Plt was better than with PRISM III, pSOFA, or Lac.Further research is still needed in the future to explore the clinical value of sTM, TAT, PIC, and t-PAI·C in diagnosis and outcome of pediatrics sepsis and pSIC.
Keywords: Children; Endothelial cell injury; Novel coagulation markers; Sepsis-induced coagulopathy; Sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Prognosis of Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023 Jan-Dec;29:10760296231195089. doi: 10.1177/10760296231195089. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023. PMID: 37605466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of soluble thrombomodulin and tissue plasminogen activator-inhibitor complex as biomarkers for prognosis and early evaluation of septic shock and sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Oct;10(10):10170-10184. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2222. Epub 2021 Sep 14. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34551574
-
Evaluation the combined diagnostic value of TAT, PIC, tPAIC, and sTM in disseminated intravascular coagulation: A multi-center prospective observational study.Thromb Res. 2019 Jan;173:20-26. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2018.11.010. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Thromb Res. 2019. PMID: 30458338
-
[Clinical value of new coagulation biomarkers in pediatric sepsis].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Mar 2;61(3):222-227. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20221018-00879. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36849348 Chinese.
-
Physical exertion induces thrombin formation and fibrin degradation in patients with peripheral atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998 Feb;18(2):244-9. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.18.2.244. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9484989 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Prognosis of Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023 Jan-Dec;29:10760296231195089. doi: 10.1177/10760296231195089. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023. PMID: 37605466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A clinical study on the screening efficacy of six thrombotic markers TAT, PIC, TM, t-PAI-C, D-D, and FDP for hypercoagulable state in pregnant women.Pak J Med Sci. 2025 Jan;41(1):189-193. doi: 10.12669/pjms.41.1.9755. Pak J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39867778 Free PMC article.
-
[Application Value of Novel Coagulation Markers in Predicting Postoperarative Complications in the Early Stage After Liver Transplantation].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Sep;54(5):1024-1029. doi: 10.12182/20230960105. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37866963 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Management Strategies in Septic Coagulopathy: A Review of the Current Literature.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;11(2):227. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11020227. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36673595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical value of TAT, PIC and t-PAIC as predictive markers for severe sepsis in pediatric patients.Front Pediatr. 2024 Mar 18;12:1336583. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1336583. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38562140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ruth A, McCracken CE, Fortenberry JD, et al. Pediatric severe sepsis: current trends and outcomes from the pediatric health information systems database. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2014;15(9):828‐838. - PubMed
-
- Levi M, de Jonge E, van der Poll T. Sepsis and disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2003;16(1-2):43‐47. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

