Long non-coding RNA HLA-F antisense RNA 1 inhibits the maturation of microRNA-613 in polycystic ovary syndrome to promote ovarian granulosa cell proliferation and inhibit cell apoptosis
- PMID: 35603775
- PMCID: PMC9275988
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2070965
Long non-coding RNA HLA-F antisense RNA 1 inhibits the maturation of microRNA-613 in polycystic ovary syndrome to promote ovarian granulosa cell proliferation and inhibit cell apoptosis
Abstract
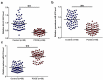
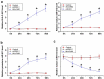
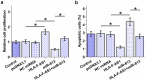
MicroRNA-613 (miR-613) inhibits granulosa cell proliferation, suggesting its involvement in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). We predicted that long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) HLA-F antisense RNA 1 (HLA-F-AS1) could interact with premature miR-613. We then explored the crosstalk between HLA-F-AS1 and miR-613 in PCOS. In this study, follicular fluid donated by 58 healthy controls and 58 PCOS patients was used to analyze the expression of HLA-F-AS1 and miR-613 (mature and premature). The direct interaction between HLA-F-AS1 and premature miR-613 was evaluated by RNA pull-down assay. Overexpression of both HLA-F-AS1 and miR-613 was achieved in granulosa cells to assess their interactions. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were detected with BrdU assay and cell apoptosis assay, respectively. We found that miR-613 was highly expressed in PCOS, while HLA-F-AS1 was downregulated in PCOS. HLA-F-AS1 directly interacted with premature miR-613, and overexpression of HLA-F-AS1 increased the expression levels of premature miR-613, but decreased the expression levels of mature miR-613. HLA-F-AS1 increased ovarian granulosa cell proliferation and inhibited cell apoptosis. MiR-613 played an opposite role and suppressed the role of HLA-F-AS1. Therefore, HLA-F-AS1 may inhibit the maturation of miR-613 in PCOS to promote ovarian granulosa cell proliferation and inhibit cell apoptosis.
Keywords: HLA-F-AS1; Polycystic ovary syndrome; apoptosis; miR-613; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
The long non-coding RNA BBOX1 antisense RNA 1 is upregulated in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and suppresses the role of microRNA-19b in the proliferation of ovarian granulose cells : Short title: BBOX1 antisense RNA 1 in cell proliferation.BMC Womens Health. 2023 Sep 21;23(1):508. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02632-5. BMC Womens Health. 2023. PMID: 37735639 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulating lncRNA NEAT1 induces proliferation and represses apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells in polycystic ovary syndrome via microRNA-381/IGF1 axis.J Biomed Sci. 2021 Jul 15;28(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12929-021-00749-z. J Biomed Sci. 2021. Retraction in: J Biomed Sci. 2022 Mar 30;29(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00805-2. PMID: 34266430 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
CDKN2B-AS1 is overexpressed in polycystic ovary syndrome and sponges miR-181a to promote granulosa cell proliferation.Anticancer Drugs. 2023 Feb 1;34(2):207-213. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001405. Epub 2023 Oct 24. Anticancer Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36622742 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs in polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021 Jan 14;19(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12958-020-00687-9. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33446212 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of MicroRNA, Long Non-Coding RNA and Circular RNA in the Pathogenesis of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Literature Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 11;25(2):903. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020903. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The long non-coding RNA BBOX1 antisense RNA 1 is upregulated in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and suppresses the role of microRNA-19b in the proliferation of ovarian granulose cells : Short title: BBOX1 antisense RNA 1 in cell proliferation.BMC Womens Health. 2023 Sep 21;23(1):508. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02632-5. BMC Womens Health. 2023. PMID: 37735639 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray-based analysis reveals a novel role of the miRNA-613/SNAI2/CXCR4 axis in atrial fibrillation.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 23;20(6):e0324324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324324. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40549746 Free PMC article.
-
Potentials as biomarker and therapeutic target of upregulated long non-coding RNA HLA-F antisense RNA 1 in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.Virus Genes. 2024 Jun;60(3):243-250. doi: 10.1007/s11262-024-02065-8. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Virus Genes. 2024. PMID: 38568442
-
HOXC Cluster Antisense RNA 3, a Novel Long Non-Coding RNA as an Oncological Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Human Malignancies.Onco Targets Ther. 2023 Oct 24;16:849-865. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S425523. eCollection 2023. Onco Targets Ther. 2023. PMID: 37899986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whispers of the polycystic ovary syndrome theater: Directing role of long noncoding RNAs.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 May 14;9(4):1023-1032. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.05.003. eCollection 2024 Dec. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39022674 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Escobar-Morreale HF. Polycystic ovary syndrome: definition, aetiology, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(5):270–284. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert EW, Tay CT, Hiam DS, et al. Comorbidities and complications of polycystic ovary syndrome: an overview of systematic reviews. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2018;89(6):683–699. - PubMed
-
- Bahri Khomami M, Joham AE, Boyle JA, et al. Increased maternal pregnancy complications in polycystic ovary syndrome appear to be independent of obesity-A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Obes Rev. 2019;20(5):659–674. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
