Bap1/SMN axis in Dpp4+ skeletal muscle mesenchymal cells regulates the neuromuscular system
- PMID: 35603786
- PMCID: PMC9220848
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.158380
Bap1/SMN axis in Dpp4+ skeletal muscle mesenchymal cells regulates the neuromuscular system
Abstract
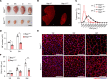
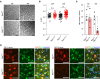
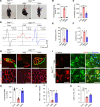
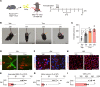
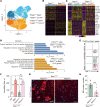
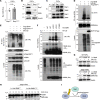
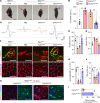
The survival of motor neuron (SMN) protein is a major component of the pre-mRNA splicing machinery and is required for RNA metabolism. Although SMN has been considered a fundamental gene for the central nervous system, due to its relationship with neuromuscular diseases, such as spinal muscular atrophy, recent studies have also revealed the requirement of SMN in non-neuronal cells in the peripheral regions. Here, we report that the fibro-adipogenic progenitor subpopulation expressing Dpp4 (Dpp4+ FAPs) is required for the neuromuscular system. Furthermore, we also reveal that BRCA1-associated protein-1 (Bap1) is crucial for the stabilization of SMN in FAPs by preventing its ubiquitination-dependent degradation. Inactivation of Bap1 in FAPs decreased SMN levels and accompanied degeneration of the neuromuscular junction, leading to loss of motor neurons and muscle atrophy. Overexpression of the ubiquitination-resistant SMN variant, SMNK186R, in Bap1-null FAPs completely prevented neuromuscular degeneration. In addition, transplantation of Dpp4+ FAPs, but not Dpp4- FAPs, completely rescued neuromuscular defects. Our data reveal the crucial role of Bap1-mediated SMN stabilization in Dpp4+ FAPs for the neuromuscular system and provide the possibility of cell-based therapeutics to treat neuromuscular diseases.
Keywords: Cell Biology; Mouse models; Muscle; Muscle Biology; Neurodegeneration.
Figures

References
-
- Park GH, et al. Reduced survival of motor neuron (SMN) protein in motor neuronal progenitors functions cell autonomously to cause spinal muscular atrophy in model mice expressing the human centromeric (SMN2) gene. J Neurosci. 2010;30(36):12005–12019. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2208-10.2010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

