In vitro inhibition of cancer angiogenesis and migration by a nanobody that targets the orphan receptor Tie1
- PMID: 35604495
- PMCID: PMC11072481
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-022-04336-9
In vitro inhibition of cancer angiogenesis and migration by a nanobody that targets the orphan receptor Tie1
Abstract
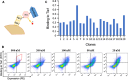
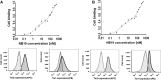
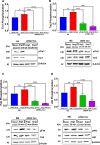
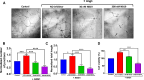
The human signaling molecules Tie1 and Tie2 receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) play important pathophysiological roles in many diseases, including different cancers. The activity of Tie1 is mediated mainly through the downstream angiopoietin-1 (Ang1)-dependent activation of Tie2, rendering both Tie 1 and the Tie1/Tie2/Ang1 axis attractive putative targets for therapeutic intervention. However, the development of inhibitors that target Tie1 and an understanding of their effect on Tie2 and on the Tie1/Tie2/Ang1 axis remain unfulfilled tasks, due, largely, to the facts that Tie1 is an orphan receptor and is difficult to produce and use in the quantities required for immune antibody library screens. In a search for a selective inhibitor of this orphan receptor, we sought to exploit the advantages (e.g., small size that allows binding to hidden epitopes) of non-immune nanobodies and to simultaneously overcome their limitations (i.e., low expression and stability). We thus performed expression, stability, and affinity screens of yeast-surface-displayed naïve and predesigned synthetic (non-immune) nanobody libraries against the Tie1 extracellular domain. The screens yielded a nanobody with high expression and good affinity and specificity for Tie1, thereby yielding preferential binding for Tie1 over Tie2. The stability, selectivity, potency, and therapeutic potential of this synthetic nanobody were profiled using in vitro and cell-based assays. The nanobody triggered Tie1-dependent inhibition of RTK (Tie2, Akt, and Fak) phosphorylation and angiogenesis in endothelial cells, as well as suppression of human glioblastoma cell viability and migration. This study opens the way to developing nanobodies as therapeutics for different cancers associated with Tie1 activation.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cell migration; Nanobody; Protein engineering; Receptor tyrosine kinase; Tie1.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activation of the orphan endothelial receptor Tie1 modifies Tie2-mediated intracellular signaling and cell survival.FASEB J. 2007 Oct;21(12):3171-83. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-8487com. Epub 2007 May 15. FASEB J. 2007. PMID: 17504972
-
Tie1 controls angiopoietin function in vascular remodeling and inflammation.J Clin Invest. 2016 Sep 1;126(9):3495-510. doi: 10.1172/JCI84923. Epub 2016 Aug 22. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27548530 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the receptor tyrosine kinases Tie1 and Tie2 in mediating the effects of angiopoietin-1 on endothelial permeability and apoptosis.Microvasc Res. 2009 Mar;77(2):187-91. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2008.09.003. Epub 2008 Sep 20. Microvasc Res. 2009. PMID: 18848573
-
Role of Angiopoietin-2 in Vascular Physiology and Pathophysiology.Cells. 2019 May 17;8(5):471. doi: 10.3390/cells8050471. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31108880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiopoietin-1/Tie2 receptor signaling in vascular quiescence and angiogenesis.Histol Histopathol. 2010 Mar;25(3):387-96. doi: 10.14670/HH-25.387. Histol Histopathol. 2010. PMID: 20054809 Review.
Cited by
-
Small Antibodies with Big Applications: Nanobody-Based Cancer Diagnostics and Therapeutics.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 29;15(23):5639. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235639. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene expression profiling and the isocitrate dehydrogenase mutational landscape of temozolomide‑resistant glioblastoma.Oncol Lett. 2024 Jun 17;28(2):378. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14511. eCollection 2024 Aug. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38939621 Free PMC article.
-
TIE1 promotes cervical cancer progression via Basigin-matrix metalloproteinase axis.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Apr 8;20(6):2297-2309. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.93667. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38617545 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative Approaches in Cancer Treatment: Emphasizing the Role of Nanomaterials in Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jun 16;17(6):783. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060783. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40574095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promising Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches Based on VHHs for Cancer Management.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 15;16(2):371. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020371. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

