Mothers' hygiene experiences in confinement centres: A cohort study
- PMID: 35604895
- PMCID: PMC9126405
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268676
Mothers' hygiene experiences in confinement centres: A cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: Ethnic Malaysian Chinese used to observe the 1-month postpartum confinement period at home and many families would engage a traditional postpartum carer to help care for the mother and newborn. A recent trend has been the development of confinement centres (CCs) which are private non-healthcare establishments run by staff not trained in health care. Concerns about hygiene in CCs arose after infections were reported. We describe the practice of hand hygiene observed in CCs, the availability of resources for hygiene, and the prevalence of health-related problems in CCs.
Methods: This is a cohort study of ethnic Chinese mothers intending to breastfeed their healthy infants. They were recruited post-delivery along with a comparison group who planned to spend their confinement period at home. After their 1-month confinement period, they were contacted for a structured telephone interview about their experience. To avoid any alteration in behaviour, mothers were not told at recruitment that they had to observe hygiene practices. Multiple logistic regression was used to assess the effect of place of confinement on rates of infant health problems.
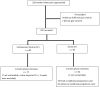
Results: Of 187 mothers, 88(47%) went to 27 different CCs while 99(53%) stayed at home. Response rates for the 1-month interviews were 88%(CC) versus 97%(home). Mothers in CC group stayed in one to four-bedded rooms and 92% of them had their baby sleeping separately in a common nursery described to have up to 17 babies at a time; 74% of them spent less than six hours a day with their babies; 43% noticed that CC staff had inadequate hand hygiene practices; 66% reported no hand basins in their rooms; 30% reported no soap at hand basins; 28% reported inexperienced or inadequate staff and 4% reported baby item sharing. Among the mothers staying at home, 35% employed a traditional postpartum carer for her baby; 32% did not room-in with their babies, but only 11% spent less than 6 hours a day with their babies. Of mothers who employed traditional postpartum carers, 32% did not know if their carer washed hands after changing diapers and 18% reported that their carer did not. Health problems that were probably related to infection (HPRI) like fever and cough were similar between the groups: 14%(CC) versus 14%(home) (p = 0.86). Multiple logistic regression did not show that CCs were a factor for HPRI: aOR 1.28 (95% CI 0.36 to 4.49). Three mothers reported events that could indicate transmission of infection in CCs.
Conclusion: We found unsatisfactory hygiene practices in CCs as reported by mothers who spent their confinement period there. Although we were not able to establish any direct evidence of infection transmission but based on reports given by the mothers in this study, it is likely to be happening. Therefore, future studies, including intervention studies, are urgently needed to establish an appropriate hygiene standard in CCs as well as the best method to implement this standard. Training CC staff with hygiene knowledge so that they can be empowered to contribute to the development of these standards would be important.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparing breastfeeding experiences between mothers spending the traditional Chinese confinement period in a confinement centre and those staying at home: a cohort study.Int Breastfeed J. 2021 Jan 6;16(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13006-020-00353-1. Int Breastfeed J. 2021. PMID: 33407645 Free PMC article.
-
Myth of the marsupial mother: home care of very low birth weight babies in Bogota, Colombia.Lancet. 1985 May 25;1(8439):1206-8. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92877-6. Lancet. 1985. PMID: 2860400
-
A Comparison of Practices During the Confinement Period among Chinese, Malay, and Indian Mothers in Singapore.Birth. 2016 Sep;43(3):247-54. doi: 10.1111/birt.12233. Epub 2016 Mar 27. Birth. 2016. PMID: 27018256 Free PMC article.
-
Impact and sustainability of a "baby friendly" health education intervention at a district hospital in Bihar, India.BMJ. 1995 Mar 11;310(6980):621-3. doi: 10.1136/bmj.310.6980.621. BMJ. 1995. PMID: 7703747 Free PMC article.
-
Cue-based versus scheduled feeding for preterm infants transitioning from tube to oral feeding: the Cubs mixed-methods feasibility study.Health Technol Assess. 2021 Dec;25(74):1-146. doi: 10.3310/hta25740. Health Technol Assess. 2021. PMID: 34878383
Cited by
-
A Participatory, Needs-Based Approach to Breastfeeding Training for Confinement Centres.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 1;19(17):10914. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191710914. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36078639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen CZ. Chinese medicine for postpartum care. Taiwan: Linking Publishing Co. Ltd; 2009.
-
- Wu DX. Zhong Yi Ji Chu Li Lun. Shanghai, China: Shanghai Ke Ji Chu Ban She; 1995. 194 p.

