Reliability of Modified Radiographic Union Score for Tibia Scores in the Evaluation of Femoral Shaft Fractures in a Low-resource Setting
- PMID: 35605095
- PMCID: PMC9126518
- DOI: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00211
Reliability of Modified Radiographic Union Score for Tibia Scores in the Evaluation of Femoral Shaft Fractures in a Low-resource Setting
Abstract
Introduction: The modified Radiographic Union Score for Tibia (RUST) fractures was developed to better describe fracture healing, but its utility in resource-limited settings is poorly understood. This study aimed to determine the validity of mRUST scores in evaluating fracture healing in diaphyseal femur fractures treated operatively at a single tertiary referral hospital in Tanzania.
Methods: Radiographs of 297 fractures were evaluated using the mRUST score and compared with outcomes including revision surgery and EuroQol five dimensions questionnaire (EQ-5D) and visual analog scale (VAS) quality-of-life measures. Convergent validity was assessed by correlating mRUST scores with EQ-5D and VAS scores. Divergent validity was assessed by comparing mRUST scores in patients based on revision surgery status.
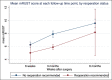
Results: The mRUST score had moderate correlation (Spearman correlation coefficient 0.40) with EQ-5D scores and weak correlation (Spearman correlation coefficient 0.320) with VAS scores. Compared with patients who required revision surgery, patients who did not require revision surgery had higher RUST scores at all time points, with statistically significant differences at 3 months (2.02, P < 0.05).
Discussion: These results demonstrate that the mRUST score is a valid method of evaluating the healing of femoral shaft fractures in resource-limited settings, with high interrater reliability, correlation with widely used quality of life measures (EQ-5D and VAS), and expected divergence in the setting of complications requiring revision surgery.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Figures
References
-
- Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R, et al. : Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380:2197-2223. - PubMed
-
- Miclau TA, Chomsky-Higgins K, Ceballos A, et al. : Building surgical research capacity globally: Efficacy of a clinical research course for surgeons in low-resource settings. Front Educ 2017;2:57.
-
- Joshipura M, Gosselin RA: Surgical burden of musculoskeletal conditions in low- and middle-income countries. World J Surg 2020;44:1026-1032. - PubMed
-
- Ghaffar A, IJsselmuiden C, Zicker F: Research capacity strengthening in low- and middle-income countries. https://www.who.int/tdr/publications/documents/changing_mindsets.pdf. Accessed May 25, 2021.