Dexmedetomidine Leads to the Mitigation of Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Diabetic Rats Via Modulation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α
- PMID: 35605218
- PMCID: PMC9162414
- DOI: 10.21470/1678-9741-2020-0591
Dexmedetomidine Leads to the Mitigation of Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Diabetic Rats Via Modulation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α
Abstract
Introduction: The objective of this study is to investigate the protective mechanism of dexmedetomidine (Dex) in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (MIR)-induced acute lung injury (ALI) of diabetic rats by inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α).
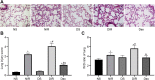
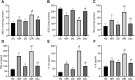
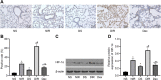
Methods: Initially, healthy male Sprague Dawley rats were treated with streptozocin to induce diabetes. Then, three weeks after the induction, Dex or lentiviral vector (LV)-HIF-1α was injected into the rats 30 minutes prior to the MIR modeling. After four weeks, lung tissues were harvested for pathological changes observation and the wet/dry weight (W/D) ratio determination. Afterwards, oxidative stress indicators and pro-inflammatory factors were measured. In addition, HIF-1α expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry and western blot analysis.
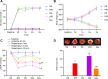
Results: Dex could suppress inflammatory cell infiltration, improve lung tissue structure, reduce pathological score and the W/D ratio, and block oxidative stress and inflammatory response in MIR-induced ALI of diabetic rats. Besides, Dex could also inhibit HIF-1α expression. Moreover, Dex + LV-HIF-1α reversed the protective role of Dex on diabetic MIR-induced ALI.
Conclusion: Our study has made it clear that Dex inhibited the upregulation of HIF-1α in diabetic MIR-induced ALI, and thus protect lung functions by quenching the accumulation of oxygen radical and reducing lung inflammatory response.
Keywords: Acute Lung Injury; Dexmedetomidine; Diabetes; Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1; Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion; Up-Regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride up-regulates expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1α to alleviate renal ischemiareperfusion injury in diabetic rats].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019 Aug 30;39(8):944-949. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.08.11. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31511215 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Dexmedetomidine post-treatment attenuates cardiac ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting apoptosis through HIF-1α signalling.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jan;24(1):850-861. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14795. Epub 2019 Nov 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31680420 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine alleviates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by activating PI3K/Akt pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jan;23(1):370-377. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201901_16785. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30657579
-
Protective effects of dexmedetomidine in vital organ injury: crucial roles of autophagy.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 May 4;27(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00335-7. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35508984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amelioration of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in diabetes: A narrative review of the mechanisms and clinical applications of dexmedetomidine.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 31;13:949754. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.949754. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120296 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
