Safety and immunogenicity of heterologous boost immunisation with an orally administered aerosolised Ad5-nCoV after two-dose priming with an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in Chinese adults: a randomised, open-label, single-centre trial
- PMID: 35605625
- PMCID: PMC9122540
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00087-X
Safety and immunogenicity of heterologous boost immunisation with an orally administered aerosolised Ad5-nCoV after two-dose priming with an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in Chinese adults: a randomised, open-label, single-centre trial
Abstract
Background: Due to waning immunity and protection against infection with SARS-CoV-2, a third dose of a homologous or heterologous COVID-19 vaccine has been proposed by health agencies for individuals who were previously primed with two doses of an inactivated COVID-19 vaccine.
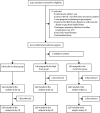
Methods: We did a randomised, open-label, controlled trial to evaluate the safety and immunogenicity of heterologous boost immunisation with an orally administered aerosolised adenovirus type-5 vector-based COVID-19 vaccine (Ad5-nCoV) in Chinese adults (≥18 years old) who had previously received two doses of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-Sinovac CoronaVac. Eligible participants were randomly assigned (1:1:1) to receive a heterologous booster vaccination with a low dose (1·0 × 1011 viral particles per mL; 0·1 mL; low dose group), or a high dose (1·0 × 1011 viral particles per mL; 0·2 mL; high dose group) aerosolised Ad5-nCoV, or a homologous intramuscular vaccination with CoronaVac (0·5 mL). Only laboratory staff were masked to group assignment. The primary endpoint for safety was the incidence of adverse reactions within 14 days after the booster dose. The primary endpoint for immunogenicity was the geometric mean titres (GMTs) of serum neutralising antibodies (NAbs) against live SARS-CoV-2 virus 14 days after the booster dose. This study was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT05043259.
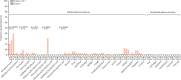
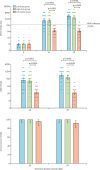
Findings: Between Sept 14 and 16, 2021, 420 participants were enrolled: 140 (33%) participants per group. Adverse reactions were reported by 26 (19%) participants in the low dose group and 33 (24%) in the high dose group within 14 days after the booster vaccination, significantly less than the 54 (39%) participants in the CoronaVac group (p<0·0001). The low dose group had a serum NAb GMT of 744·4 (95% CI 520·1-1065·6) and the high dose group had a GMT of 714·1 (479·4-1063·7) 14 days after booster dose, significantly higher than the GMT in the CoronaVac group (78·5 [60·5-101·7]; p<0·0001).
Interpretation: We found that a heterologous booster vaccine with an orally administered aerosolised Ad5-nCoV is safe and highly immunogenic in adults who have previously received two doses of CoronaVac as the primary series vaccination.
Funding: National Natural Science Foundation of China and Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Program.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Vaccines. 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/coronavirus-dis...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

