Association of APOE-Independent Alzheimer Disease Polygenic Risk Score With Brain Amyloid Deposition in Asymptomatic Older Adults
- PMID: 35606148
- PMCID: PMC9421597
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000200544
Association of APOE-Independent Alzheimer Disease Polygenic Risk Score With Brain Amyloid Deposition in Asymptomatic Older Adults
Abstract
Background and objectives: Brain amyloid deposition, a major risk factor for Alzheimer disease (AD), is currently estimated by measuring CSF or plasma amyloid peptide levels or by PET imaging. Assessing genetic risks relating to amyloid deposition before any accumulation has occurred would allow for earlier intervention in persons at increased risk for developing AD. Previous work linking amyloid burden and genetic risk relied almost exclusively on APOE, a major AD genetic risk factor. Here, we ask whether a polygenic risk score (PRS) that incorporates an optimized list of common variants linked to AD and excludes APOE is associated with brain amyloid load in cognitively unimpaired older adults.
Methods: We included 291 asymptomatic older participants from the INveStIGation of AlzHeimer's PredicTors (INSIGHT pre-AD) cohort who underwent amyloid imaging, including 83 amyloid-positive (+) participants. We used an Alzheimer's (A) PRS composed of 33 AD risk variants excluding APOE and selected the 17 variants that showed the strongest association with amyloid positivity to define an optimized (oA) PRS. Participants from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) study (228 participants, 90 amyloid [+]) were tested as a validation cohort. Finally, 2,300 patients with AD and 6,994 controls from the European Alzheimer's Disease Initiative (EADI) were evaluated.
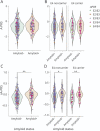
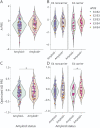
Results: A-PRS was not significantly associated with amyloid burden in the INSIGHT or ADNI cohorts with or without correction for the APOE genotype. However, oA-PRS was significantly associated with amyloid status independently of APOE adjustment (INSIGHT odds ratio [OR]: 5.26 [1.71-16.88]; ADNI OR: 3.38 [1.02-11.63]). Of interest, oA-PRS accurately discriminated amyloid (+) and (-) APOE ε4 carriers (INSIGHT OR: 181.6 [7.53-10,674.6]; ADNI OR: 44.94 [3.03-1,277]). A-PRS and oA-PRS showed a significant association with disease status in the EADI cohort (OR: 1.68 [1.53-1.85] and 2.06 [1.73-2.45], respectively). Genes assigned to oA-PRS variants were enriched in ontologies related to β-amyloid metabolism and deposition.
Discussion: PRSs relying on AD genetic risk factors excluding APOE may improve risk prediction for brain amyloid, allowing stratification of cognitively unimpaired individuals at risk of AD independent of their APOE status.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
