Prevalence and Predictors of Vascular Cognitive Impairment in Patients With CADASIL
- PMID: 35606149
- PMCID: PMC9421594
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000200607
Prevalence and Predictors of Vascular Cognitive Impairment in Patients With CADASIL
Abstract
Background and objectives: Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) is the most common monogenic form of stroke and early-onset dementia. We determined the prevalence of vascular cognitive impairment (VCI) in a group of patients with CADASIL and investigated which factors were associated with VCI risk, including clinical, genetic, and MRI parameters.
Methods: Cognition was assessed in patients with genetically confirmed CADASIL (n = 176) and healthy controls (n = 265) (mean [SD] age 50.95 [11.35] vs 52.37 [7.93] years) using the Brief Memory and Executive Test (BMET) and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA). VCI was defined according to previously validated cutoffs. We determined the prevalence of VCI and its associations with clinical risk factors, mutation location (epidermal growth factor-like repeats [EGFr] 1-6 vs EGFr 7-34), and MRI markers of small vessel disease.
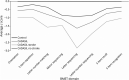
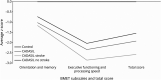
Results: VCI was more common in patients with CADASIL than in controls; 39.8 vs 10.2% on the BMET and 47.7% vs 19.6% on the MOCA. Patients with CADASIL had worse performance across all cognitive domains. A history of stroke was associated with VCI on the BMET (OR 2.12, 95% CI [1.05, 4.27] p = 0.04) and MoCA (OR 2.55 [1.21, 5.41] p = 0.01), after controlling for age and sex. There was no association of VCI with mutation site. Lacune count was the only MRI parameter independently associated with VCI on the BMET (OR: 1.63, 95% CI [1.10, 2.41], p = 0.014), after controlling for other MRI parameters. These associations persisted after controlling for education in the sensitivity analyses.
Discussion: VCI is present in almost half of the patients with CADASIL with a mean age of 50 years. Stroke and lacune count on MRI were both independent predictors of VCI on the BMET.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- Chabriat H, Joutel A, Dichgans M, Tournier-Lasserver E, Bousser M-G. CADASIL. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:643-653. - PubMed
-
- Adib-Samii P, Brice G, Martin RJ, Markus HS. Clinical spectrum of CADASIL and the effect of cardiovascular risk factors on phenotype: study in 200 consecutively recruited individuals. Stroke. 2010;41:630-634. - PubMed
-
- Dichgans M, Mayer M, Uttner I, et al. . The phenotypic spectrum of CADASIL: clinical findings in 102 cases. Ann Neurol. 1998;44(5):731-739. - PubMed
-
- Desmond DW, Moroney JT, Lynch T, Chan S, Chin SS, Mohr JP. The natural history of CADASIL: a pooled analysis of previously published cases. Stroke. 1999;30(6):1230-1233. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
