Phase 1/2 clinical trial of COVID-19 vaccine in Japanese participants: A report of interim findings
- PMID: 35606235
- PMCID: PMC9122779
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.04.054
Phase 1/2 clinical trial of COVID-19 vaccine in Japanese participants: A report of interim findings
Abstract
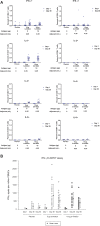
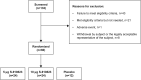
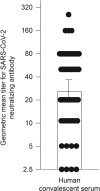
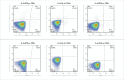
We initiated a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 trial to evaluate the safety and immunogenicity of the S-268019-b recombinant protein vaccine, scheduled as 2 intramuscular injections given 21 days apart, in 60 randomized healthy Japanese adults. We evaluated 2 regimens of the S-910823 antigen (5 μg [n = 24] and 10 μg [n = 24]) with an oil-in-water emulsion formulation and compared against placebo (n = 12). Reactogenicity was mild in most participants. No serious adverse events were noted. For both regimens, vaccination resulted in robust IgG and neutralizing antibody production at days 36 and 50 and predominant T-helper 1-mediated immune reaction, as evident through antigen-specific polyfunctional CD4+ T-cell responses with IFN-γ, IL-2, and IL-4 production on spike protein peptides stimulation. Based on the interim analysis, the S-268019-b vaccine is safe, produces neutralizing antibodies titer comparable with that in convalescent serum from COVID-19-recovered patients. However, further evaluation of the vaccine in a large clinical trial is warranted.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine; Cellular immunity; Clinical trial; Immunogenicity; Reactogenicity; Recombinant protein; Safety.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: SI received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing, and educational events from Astellas Pharma Inc., Japan Vaccine Co., Ltd., Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., and Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. TS, AK, RS, TH, SO, KI, and MA are employees of Shionogi & Co. Ltd..
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. Available from: https://covid19.who.int Last accessed: October 9, 2021.
-
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 vaccine tracker and landscape. Available from: https://covid19.who.int Last accessed: October 9, 2021.
-
- WMA Declaration of Helsinki – Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. Available from: https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-pr... Last accessed: October 9, 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

