Phenotypic and genetic associations of quantitative magnetic susceptibility in UK Biobank brain imaging
- PMID: 35606419
- PMCID: PMC9174052
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-022-01074-w
Phenotypic and genetic associations of quantitative magnetic susceptibility in UK Biobank brain imaging
Abstract
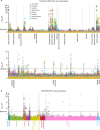
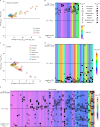
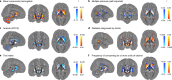
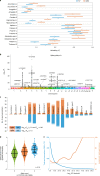
A key aim in epidemiological neuroscience is identification of markers to assess brain health and monitor therapeutic interventions. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) is an emerging magnetic resonance imaging technique that measures tissue magnetic susceptibility and has been shown to detect pathological changes in tissue iron, myelin and calcification. We present an open resource of QSM-based imaging measures of multiple brain structures in 35,273 individuals from the UK Biobank prospective epidemiological study. We identify statistically significant associations of 251 phenotypes with magnetic susceptibility that include body iron, disease, diet and alcohol consumption. Genome-wide associations relate magnetic susceptibility to 76 replicating clusters of genetic variants with biological functions involving iron, calcium, myelin and extracellular matrix. These patterns of associations include relationships that are unique to QSM, in particular being complementary to T2* signal decay time measures. These new imaging phenotypes are being integrated into the core UK Biobank measures provided to researchers worldwide, creating the potential to discover new, non-invasive markers of brain health.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Associations between moderate alcohol consumption, brain iron, and cognition in UK Biobank participants: Observational and mendelian randomization analyses.PLoS Med. 2022 Jul 14;19(7):e1004039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004039. eCollection 2022 Jul. PLoS Med. 2022. PMID: 35834561 Free PMC article.
-
An expanded set of genome-wide association studies of brain imaging phenotypes in UK Biobank.Nat Neurosci. 2021 May;24(5):737-745. doi: 10.1038/s41593-021-00826-4. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Nat Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33875891 Free PMC article.
-
MRI estimates of brain iron concentration in normal aging using quantitative susceptibility mapping.Neuroimage. 2012 Feb 1;59(3):2625-35. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.08.077. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 21925274 Free PMC article.
-
Value of Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping in Clinical Neuroradiology.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Jun;59(6):1914-1929. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29010. Epub 2023 Sep 8. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37681441 Review.
-
Wellbeing and brain structure: A comprehensive phenotypic and genetic study of image-derived phenotypes in the UK Biobank.Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 Dec 1;43(17):5180-5193. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25993. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022. PMID: 35765890 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brain Imaging and Phenotyping for the China Phenobank Project.Phenomics. 2025 Jan 2;4(6):592-593. doi: 10.1007/s43657-024-00197-3. eCollection 2024 Dec. Phenomics. 2025. PMID: 40061821 No abstract available.
-
Individualised prediction of longitudinal change in multimodal brain imaging.Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024 Jul 3;2:1-19. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00215. eCollection 2024 Jul 1. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024. PMID: 40046980 Free PMC article.
-
Association of gout with brain reserve and vulnerability to neurodegenerative disease.Nat Commun. 2023 May 18;14(1):2844. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38602-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37202397 Free PMC article.
-
Telomere length and brain imaging phenotypes in UK Biobank.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 22;18(3):e0282363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282363. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36947528 Free PMC article.
-
Hemochromatosis neural archetype reveals iron disruption in motor circuits.Sci Adv. 2024 Nov 22;10(47):eadp4431. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp4431. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39576859 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

