Prevalence of drinking or eating more than usual and associated factors during childhood diarrhea in East Africa: a multilevel analysis of recent demographic and health survey
- PMID: 35606750
- PMCID: PMC9125918
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-022-03370-7
Prevalence of drinking or eating more than usual and associated factors during childhood diarrhea in East Africa: a multilevel analysis of recent demographic and health survey
Abstract
Background: Diarrhea is the second most common cause of death in under-five children. Fluid and food replacement during diarrheal episodes have a paramount effect to avert morbidity and mortality. However, there is limited information about feeding practices. This study aimed to assess the prevalence of drinking or eating more and associated factors during diarrhea among under-five children in East Africa using demographic and health surveys (DHSs).
Methods: Secondary data analysis was done on DHSs 2008 to 2018 in 12 East African Countries. Total weighted samples of 20,559 mothers with their under-five children were included. Data cleaning, coding, and analysis were performed using Stata 16. Multilevel binary logistic regression were performed to identify factors associated with drinking or eating more during diarrheal episodes. Adjusted Odds Ratio (AOR) with a 95% CI, and p-value < 0.05 were used to declare statistical significance.
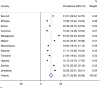
Results: Prevalence of drinking or eating more than usual during diarrhea disease in East Africa was 26.27%(95% CI: 25.68-26.88). Mothers age > 35 years (AOR: 1.14, 95% CI: (1.03, 1.26), mothers primary education (AOR: 1.17, 95% CI: 1.06,1.28), secondary education (AOR: 1.43,95% CI: 1.27,1.61), and higher education (AOR: 1.42,95% CI: 1.11,1.81), occupation of mothers (agriculture, AOR: 2.2, 95% CI: 1.3-3.6), sales and services, AOR = 1.20, CI:1.07,1.34), manual, AOR =1.28,95% CI: 1.11,1.44), children age 1-2 years (AOR =1.34,95% CI: 1.22,1.46) and 3-4 years (AOR =1.36,95% CI: 1.20,1.55), four and more antenatal visits (AOR: 1.14,95% CI: 1.03,1.27), rich wealth status (AOR:1.27,95% CI: 1.16,1.40), birth in health facility (AOR = 1.19, 95%CI: 1.10, 1.30) and visit health facility (AOR = 1.12, 95%CI: 1.03, 1.22) were associated with drinking or eating more.
Conclusion: The prevalence of drinking or eating more is low in East Africa. Maternal age, occupation, antenatal care visit, marital status, educational status, wealth status, place of delivery, visiting health facility, and child age were significantly associated with drinking or eating more during diarrheal episodes. Health policy and programs should focus on educating mothers, improving the household wealth status, encouraging women to contact health facilities for better feeding practices of children during diarrheal episodes.
Keywords: Children; Drinking or eating more; East Africa; Prevalence.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Diarrhoeal disease. Tropical doctor. 2017.
-
- Jelliffe DB, Jelliffe PEF. Dietary management of young children with acute diarrhoea. 1991.
-
- UNICEF. One is too many: ending child deaths from pneumonia and diarrhoea. New York, NY; 2016.
-
- Bhatia SK. Diarrheal Diseases. InBiomaterials for Clinical Applications. New York, NY: Springer; 2010. p. 121–45.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical