Dynamic functional connectivity patterns associated with dementia risk
- PMID: 35606867
- PMCID: PMC9128270
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-022-01006-7
Dynamic functional connectivity patterns associated with dementia risk
Abstract
Background: This study assesses the relationships between dynamic functional network connectivity (DFNC) and dementia risk.
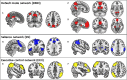
Methods: DFNC of the default mode (DMN), salience (SN), and executive control networks was assessed in 127 cognitively unimpaired older adults. Stepwise regressions were performed with dementia risk and protective factors and biomarkers as predictors of DFNC.
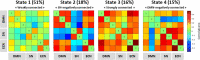
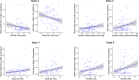
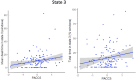
Results: Associations were found between times spent in (i) a "weakly connected" state and lower self-reported engagement in early- and mid-life cognitive activity and higher LDL cholesterol; (ii) a "SN-negatively connected" state and higher blood pressure, higher depression score, and lower body mass index (BMI); (iii) a "strongly connected" state and higher self-reported engagement in early-life cognitive activity, Preclinical Alzheimer's cognitive composite-5 score, and BMI; and (iv) a "DMN-negatively connected" state and higher self-reported engagement in early- and mid-life stimulating activities and lower LDL cholesterol and blood pressure. The lower number of state transitions was associated with lower brain perfusion.
Conclusion: DFNC states are differentially associated with dementia risk and could underlie reserve.
Keywords: Cardiovascular risk factors; Cognition; Cognitive reserve; Dementia risk; Dynamic functional network connectivity; Lifestyle; Sliding window analysis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
GC has received research support from the EU’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement number 667696), Inserm, Fondation d’entreprise MMA des Entrepreneurs du Futur, Fondation Alzheimer, Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique, Région Normandie, Association France Alzheimer et maladies apparentées and Fondation Vaincre Alzheimer (all to Inserm), and personal fees from Fondation d’entreprise MMA des Entrepreneurs du Futur. All other authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang X-X, Tian Y, Wang Z-T, Ma Y-H, Tan L, Yu J-T. The epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease modifiable risk factors and prevention. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2021:1–9. 10.14283/jpad.2021.15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

