Comparing Long-Term Survival Outcomes for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Patients Who Underwent with Radical Cystectomy and Bladder-Sparing Trimodality Therapy: A Multicentre Cohort Analysis
- PMID: 35607328
- PMCID: PMC9124076
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7306198
Comparing Long-Term Survival Outcomes for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Patients Who Underwent with Radical Cystectomy and Bladder-Sparing Trimodality Therapy: A Multicentre Cohort Analysis
Abstract
Background: Although radical cystectomy (RC) is the clinical practice guideline-recommended treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC), bladder-sparing trimodality therapy (TMT) has emerged as a valid treatment option. Findings comparing the survival outcomes for MIBC patients who underwent RC and TMT are inconclusive.
Objective: We designed a large hospital-based multicohort study to compare the effectiveness of TMT with RC.
Methods: Information on deaths was jointly retrieved from EMR (electronic medical record), cause of death registry, and chronic disease surveillance as well as study-specific questionnaire. To avoid the systematical difference between patients who received two modalities, RC-MIBC cohort was propensity score-matched to TMT-MIBC cohort, and the Cox proportional hazard regression was used to calculate the overall survival (OS) and disease-specific survival (DSS).
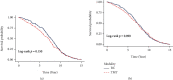
Results: There were 891 MIBC patients treated with RC and another 891 MIBC patients who underwent with TMT in the propensity score matching. Comparable effectiveness between two modalities was observed for DSS (HR, 1.20; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.94 to 1.49) and OS (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 0.91 to 1.43) according to multiple adjustment after a median follow-up of approximately 9.3 years. However, a relatively higher mortality rate around 5 years after TMT treatment was found compared to RC (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.01 to 1.53). The respective 5-year OS rates were 69% and 73% for TMT cohort and RC cohort, respectively.
Conclusions: Our findings supported that MIBC patients with TMT yielded survival outcomes comparable to MIBC patients who underwent RC overall. Treatment options should be suggested considering patients' age and willingness.
Copyright © 2022 Junlan Qiu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Propensity Score Analysis of Radical Cystectomy Versus Bladder-Sparing Trimodal Therapy in the Setting of a Multidisciplinary Bladder Cancer Clinic.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jul 10;35(20):2299-2305. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.69.2327. Epub 2017 Apr 14. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28410011
-
Impact of Immune and Stromal Infiltration on Outcomes Following Bladder-Sparing Trimodality Therapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer.Eur Urol. 2019 Jul;76(1):59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.01.011. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Eur Urol. 2019. PMID: 30712971 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of trimodality therapy and neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with radical cystectomy for the survival of muscle-invasive bladder cancer: a population-based analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Oct 11;28(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01408-9. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37822001 Free PMC article.
-
Trimodality Therapy Versus Radical Cystectomy for Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Matched Cohort Studies.Eur Urol Focus. 2024 Nov 21:S2405-4569(24)00244-X. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2024.11.003. Online ahead of print. Eur Urol Focus. 2024. PMID: 39578213 Review.
-
Organ-Sparing Strategies in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Oct 13;13:7833-7839. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S294099. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34675678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oncological effectiveness of bladder-preserving trimodal therapy versus radical cystectomy for the treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer: a system review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Aug 29;21(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-03161-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37641150 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Outcomes of Radical Cystectomy in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2023 Dec 17;15(12):e50646. doi: 10.7759/cureus.50646. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38229790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of interpretable machine learning models to predict distant metastasis and prognosis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 6;15(1):11795. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96089-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40189676 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Modality Bladder-Sparing Therapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: How (Should) We Do It? A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 16;12(4):1560. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041560. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36836093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscle-invasive bladder cancer in elderly and frail people: Is hypofractionated radiotherapy a feasible approach when no other local options are available?Tumori. 2024 Jun;110(3):193-202. doi: 10.1177/03008916241252326. Epub 2024 May 10. Tumori. 2024. PMID: 38726748 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

