Duchesnea indica Extract Ameliorates LPS-Induced Septic Shock in Mice
- PMID: 35607518
- PMCID: PMC9124116
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5783867
Duchesnea indica Extract Ameliorates LPS-Induced Septic Shock in Mice
Abstract
Objective: Duchesnea indica has been reported for its anti-inflammatory properties. However, its efficacy in sepsis has yet to be reported. In this study, we studied the ability of Duchesnea indica extract (DIE) to rescue mice from septic shock and sepsis.
Methods: In vitro studies included the measurement of secreted nitric oxide, cell viability, gene and protein expression via real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blot, and confocal microscopy in RAW 264.7 cells. In vivo studies include a model of septic shock and sepsis in BALB/c mice induced by a lethal and sub-lethal dose of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
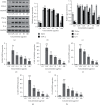
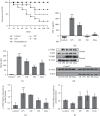
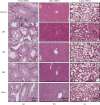
Results: DIE suppressed the expression of proinflammatory cytokines induced by LPS and prevented the translocation of NFκB into the nucleus of RAW 264.7 cells. It also prevented reactive oxygen species damage induced by LPS in murine bone marrow-derived macrophages. Models of sepsis and septic shock were established in BALB/c mice and DIE-rescued mice from septic shock. DIE also reversed the increase in tumor necrosis factor-α and nitrite levels in the serum of mice induced with sepsis. DIE also prevented the translocation of NFκB from the cytosol into the nucleus in murine lungs. Histopathological damage induced by sepsis was reversed in the testis, liver, and lungs of mice.
Conclusion: In conclusion, DIE is a suitable candidate for development as a therapeutic agent for sepsis.
Copyright © 2022 Yuan Yee Lee et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All of the authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The sesquiterpene lactone estafiatin exerts anti-inflammatory effects on macrophages and protects mice from sepsis induced by LPS and cecal ligation puncture.Phytomedicine. 2022 May;99:153934. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153934. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35172258
-
Duchesnea indica Extract Attenuates Coal Fly Ash-Induced Inflammation in Murine Alveolar Macrophages through the NF-Kappa B Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jun 4;2021:5546052. doi: 10.1155/2021/5546052. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34194518 Free PMC article.
-
α-Solanine Isolated From Solanum Tuberosum L. cv Jayoung Abrogates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses Via NF-κB Inactivation in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and Endotoxin-Induced Shock Model in Mice.J Cell Biochem. 2016 Oct;117(10):2327-39. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25530. Epub 2016 Mar 11. J Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26931732
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of Acalypha australis L. via suppression of NF-κB signaling in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and LPS-induced septic mice.Mol Immunol. 2020 Mar;119:123-131. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.01.010. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32014631
-
In vitro and in vivo therapeutics of β-thujaplicin on LPS-induced inflammation in macrophages and septic shock in mice.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012 Jan-Mar;25(1):39-48. doi: 10.1177/039463201202500106. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22507316
Cited by
-
Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Duchesnea indica Extracts Using Different Solvents and Their Antibacterial Activity.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 9;11(6):1539. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11061539. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37375043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang L., Li S., Liu H., Bao L. Advances in research on the effects of natural drugs with immune-promoting effects on immune function. European Journal of Inflammation . 2020;18 doi: 10.1177/2058739220926878.205873922092687 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

