Novel 2-(5-Aryl-4,5-Dihydropyrazol-1-yl)thiazol-4-One as EGFR Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Assessment and Molecular Docking Insights
- PMID: 35607598
- PMCID: PMC9123247
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S356988
Novel 2-(5-Aryl-4,5-Dihydropyrazol-1-yl)thiazol-4-One as EGFR Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Assessment and Molecular Docking Insights
Abstract
Introduction: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) regulates several cell functions which include cell growth, survival, multiplication, differentiation, and apoptosis. Currently, EGFR kinase inhibitors are of increasing interest as promising targeted antitumor therapeutic agents.
Methods: Different thiazolyl-pyrazoline derivatives (7a-o) were synthesized and were first tested for anti-proliferative effect towards the A549 lung cancer cell line and the T-47D breast cancer cell line in MTT assay. Thereafter, thiazolyl-pyrazolines (7b, 7g, 7l, and 7m) were subsequently evaluated for their PK inhibition for EGFR. Moreover, representative promising derivatives (7g and 7m) in cytotoxic and PK inhibition assays were tested to investigate their impact on the apoptosis and cell cycle phases in T-47D cells in order to explore more insights into the antitumor actions of the target thiazolyl-pyrazolines. Furthermore, docking studies were accomplished to evaluate the patterns of binding of thiazolyl-pyrazolines 7b, 7g, 7l, and 7m in the EGFR active pocket (PDB ID: 1M17).
Results: Testing the thiazolyl pyrazoline compounds 7a-o on A549 and T-47D cell lines showed IC50 arrays between 3.92 and 89.03 µM, and between 0.75 and 77.10 µM, respectively. Also, the tested thiazolyl-pyrazolines (7b, 7g, 7l, and 7m) demonstrated significant sub-micromolar EGFR inhibitory actions with IC50 values 83, 262, 171 and 305 nM, respectively, in comparison to erlotinib (IC50 =57 nM).
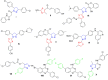
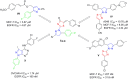
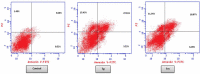
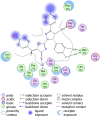
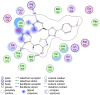
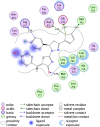
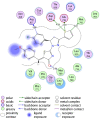
Discussion: Generally, it was observed that the tested thiazolyl pyrazolines showed more potent antiproliferative activity toward breast cancer cells T-47D than toward lung cancer cell lines A549. In particular, thiazolyl pyrazolines 7g and 7m showed the best activity against A549 cells (IC50 = 3.92 and 6.53 µM) and T-47D cells (IC50 = 0.88 and 0.75 µM). Compounds 7g and 7m provoked a sub-G1 phase arrest and cell apoptosis which are in agreement with the expected outcome of EGFR inhibition. Finally, the molecular docking of 7g and 7m in the active site of EGFR revealed a common binding pattern similar to that of erlotinib which involves the accommodation of the 1,3 thiazol-4-one ring and pyrazoline ring of target compounds in the binding region of erlotinib's quinazoline ring and anilino moiety.
Keywords: EGFR inhibitors; antitumor; breast cancer; lung cancer; molecular docking; pyrazolo.
© 2022 Al-Warhi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
New Thiazolyl-Pyrazoline Derivatives as Potential Dual EGFR/HER2 Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Anticancer Activity Evaluation and In Silico Study.Molecules. 2023 Nov 6;28(21):7455. doi: 10.3390/molecules28217455. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37959874 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of a new series of thiazolyl-pyrazolines as dual EGFR and HER2 inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Nov 15;182:111648. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111648. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31493743
-
Synthesis of S-alkylated oxadiazole bearing imidazo[2,1-b]thiazole derivatives targeting breast cancer: In vitro cytotoxic evaluation and in vivo radioactive tracing studies.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Dec;153:107935. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107935. Epub 2024 Nov 2. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 39504637
-
Novel benzothiazole-based dual VEGFR-2/EGFR inhibitors targeting breast and liver cancers: Synthesis, cytotoxic activity, QSAR and molecular docking studies.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022 Feb 15;58:128529. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128529. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35007724 Review.
-
2-Anilinopyrimidine derivatives: Design, synthesis, in vitro anti-proliferative activity, EGFR and ARO inhibitory activity, cell cycle analysis and molecular docking study.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Jun;99:103798. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103798. Epub 2020 Mar 29. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32247112 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of novel thiazolyl-pyrazolines as dual EGFR and VEGFR-2 inhibitors endowed with in vitro antitumor activity towards non-small lung cancer.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):2265-2282. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2104841. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36000167 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of hexahydroquinoline as anticancer scaffold targeting inhibition of wild and mutants EGFR (EGFRWT, EGFRT790M, and EGFRL858R).J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2241674. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2241674. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37548154 Free PMC article.
-
Recent studies on protein kinase signaling inhibitors based on thiazoles: review to date.RSC Adv. 2024 Nov 19;14(50):36989-37018. doi: 10.1039/d4ra05601a. eCollection 2024 Nov 19. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39569127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine Learning, Molecular Docking, and Dynamics-Based Computational Identification of Potential Inhibitors against Lung Cancer.ACS Omega. 2024 Jan 17;9(4):4528-4539. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c07338. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38313551 Free PMC article.
-
New Thiazolyl-Pyrazoline Derivatives as Potential Dual EGFR/HER2 Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Anticancer Activity Evaluation and In Silico Study.Molecules. 2023 Nov 6;28(21):7455. doi: 10.3390/molecules28217455. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37959874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim SK, Kalimuthu S. Introduction to anticancer drugs from marine origin. In: Handbook of Anticancer Drugs from Marine Origin. Cham: Springer; 2015:1–13.
-
- Ferlay J. GLOBOCAN 2008 v1. 2, cancer incidence and mortality world-wide: IARC Cancer Base No. 10; 2010. Available from: http://globocan.iarc. Accessed April 16, 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

