An open-source, automated, gas sampling peripheral for laboratory incubation experiments using cavity ring-down spectroscopy
- PMID: 35607691
- PMCID: PMC9123425
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ohx.2021.e00208
An open-source, automated, gas sampling peripheral for laboratory incubation experiments using cavity ring-down spectroscopy
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "An open-source, automated, gas sampling peripheral for laboratory incubation experiments using cavity ring-down spectroscopy" [HardwareX 10 (2021) e00208].HardwareX. 2024 Feb 9;17:e00514. doi: 10.1016/j.ohx.2024.e00514. eCollection 2024 Mar. HardwareX. 2024. PMID: 38414730 Free PMC article.
Abstract
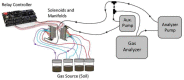
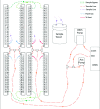
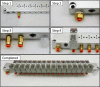
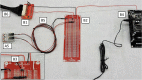
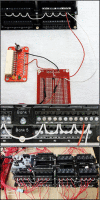
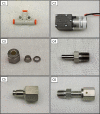
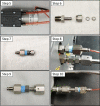
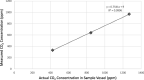
Spectroscopic instruments are becoming increasingly popular for measuring the isotopic composition and fluxes of a wide variety of gases in both field and laboratory experiments. The popularity of these instruments has created a need for automated multiplexers compatible with the equipment. While there are several such peripherals commercially available, they are currently limited to only a small number of samples (≤16), which is insufficient for some studies. To support researchers in constructing custom, larger-scale systems, we present our design for a scalable gas sampling peripheral that can be programmed to autonomously sample up to 56 vessels - the "multiplexer". While originally designed to be used with a Picarro cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) system, the multiplexer design and data processing approach implemented can be easily adapted to serve as a gas sampling/delivery platform for a wide variety of instruments including other cavity ring-down systems and infra-red gas analyzers. We demonstrate the basic capabilities of the multiplexer by using it to autonomously sample head-space CO2 from 14 laboratory-incubated soils amended with 13C-enriched pyrogenic organic matter for analysis in a Picarro G2201-i cavity ring-down spectroscopy system.
Keywords: Autosampler; Cavity ring-down spectroscopy; Gas sampling; Respiration study; Soil gas fluxes; Trace gas analysis.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Nickerson and Creelman are employed by Eosense Inc., a for-profit company that produces gas multiplexer units for similar applications. No additional interests are present.
Figures













References
-
- Zalicki P., Zare R.N. Cavity ring-down spectroscopy for quantitative absorption-measurements. J. Chem. Phys. 1995;102(7):2708–2717.
-
- Crosson E.R., et al. Stable isotope ratios using cavity ring-down spectroscopy: determination of 13C/12C for carbon dioxide in human breath. Anal. Chem. 2002;74(9):2003–2007. - PubMed
-
- Midwood A.J., Millard P. Challenges in measuring the delta C-13 of the soil surface CO2 efflux. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011;25(1):232–242. - PubMed
-
- Kerstel E., Gianfrani L. Advances in laser-based isotope ratio measurements: selected applications. Appl. Phys. B-Lasers and Optics. 2008;92(3):439–449.
-
- Robinson, David and Alex Hayes, Broom: Convert statistical analysis objects into tidy tibbles. 2018. R package: version 0.5.0.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

