Increasing Brain Gamma Activity Improves Episodic Memory and Restores Cholinergic Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 35607946
- PMCID: PMC9546168
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.26411
Increasing Brain Gamma Activity Improves Episodic Memory and Restores Cholinergic Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess whether non-invasive brain stimulation with transcranial alternating current stimulation at gamma-frequency (γ-tACS) applied over the precuneus can improve episodic memory and modulate cholinergic transmission by modulating cerebral rhythms in early Alzheimer's disease (AD).
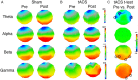
Methods: In this randomized, double-blind, sham controlled, crossover study, 60 AD patients underwent a clinical and neurophysiological evaluation including assessment of episodic memory and cholinergic transmission pre and post 60 minutes treatment with γ-tACS targeting the precuneus or sham tACS. In a subset of 10 patients, EEG analysis and individualized modelling of electric field distribution were carried out. Predictors to γ-tACS efficacy were evaluated.
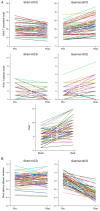
Results: We observed a significant improvement in the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning (RAVL) test immediate recall (p < 0.001) and delayed recall scores (p < 0.001) after γ-tACS but not after sham tACS. Face-name associations scores improved with γ-tACS (p < 0.001) but not after sham tACS. Short latency afferent inhibition, an indirect measure of cholinergic transmission, increased only after γ-tACS (p < 0.001). ApoE genotype and baseline cognitive impairment were the best predictors of response to γ-tACS. Clinical improvement correlated with the increase in gamma frequencies in posterior regions and with the amount of predicted electric field distribution in the precuneus.
Interpretation: Precuneus γ-tACS, able to increase γ-power activity on the posterior brain regions, showed a significant improvement of episodic memory performances, along with restoration of intracortical excitability measures of cholinergic transmission. Response to γ-tACS was dependent on genetic factors and disease stage. ANN NEUROL 2022;92:322-334.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04842955.
© 2022 The Authors. Annals of Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
A.B. and B.B. have pending patent on the use of non‐invasive brain stimulation to increase memory functions in patients with Alzheimer Disease.
Figures
References
-
- FDA Grants Accelerated Approval for Alzheimer's Drug [Internet] . 2021. [cited 2021 Jul 6 ] Available from: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-grants-accelerat...
-
- Koenig T, Prichep L, Dierks T, et al. Decreased EEG synchronization in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment [internet]. Neurobiol Aging 2005;26:165–171.[cited 2019 Oct 9 ] Available from:. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0197458004001538?via%.... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

