Lymphoepithelial cyst in the palatine tonsil: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 35608426
- PMCID: PMC9276245
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029246
Lymphoepithelial cyst in the palatine tonsil: A case report and literature review
Abstract
Rationale: Lymphoepithelial cyst of the oral cavity is very rare. Most intraoral lymphoepithelial cysts are observed in the floor of the mouth and very few cases have been reported of its occurrence in the palatine tonsil.
Patient concerns: A 37-year-old healthy woman with no remarkable medical history visited our department with a complaint of frequent tonsillitis.
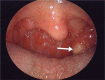
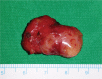
Interventions: On endoscopic examination, yellowish mass was observed in the palatine tonsil and removed via an intraoral approach. The mass was completely removed with the left palatine tonsil.
Diagnoses outcomes: Histopathological examination and immunohistochemical staining confirmed a Lymphoepithelial cyst.
Lessons: Lymphepithelial cysts of the palatine tonsils are extremely rare and are easily overlooked because there are few reported cases. Therefore, care must be taken when examining the tonsil mass.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Yang X, Ow A, Zhang CP, et al. . Clinical analysis of 120 cases of intraoral lymphoepithelial cyst. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2012;113:448–52. - PubMed
-
- Giunta J, Cataldo E. Lymphoepithelial cysts of the oral mucosa. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1973;35:77–84. - PubMed
-
- Knapp MJ. Pathology of oral tonsils. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1970;29:295–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

