Overall Survival in Phase 3 Clinical Trials and the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer, 1986-2016: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35608860
- PMCID: PMC9131746
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.13588
Overall Survival in Phase 3 Clinical Trials and the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer, 1986-2016: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Importance: Phase 3 trials for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) have been conducted with varying designs and often with surrogate end points for overall survival (OS).
Objectives: To critically examine the factors associated with clinically relevant improvement in OS (defined as ≥2 months) in these trials and to evaluate their association with outcomes reflected in Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registry data.
Evidence review: Medline, EMBASE, Cochrane, Web of Science, ClinicalTrials.gov, EU Clinical Trials Register, and the International Clinical Trials Registry Platform were searched for phase 3 trials of systemic therapy for patients with mCRC by decade (1986-1996, 1997-2006, and 2007-2016), excluding early or pilot studies, studies that did not involve an anticancer drug, studies on cancer screening and prevention, reports of pooled data from multiple trials, and studies with nonpharmaceutical approaches. The association of drug development with OS outside the clinical trial setting was evaluated using data from the SEER registry, including adult patients with a primary cancer site in the colon or rectum, including adenocarcinoma, mucinous adenocarcinoma, or signet ring cell carcinoma; a distant stage; and receipt of chemotherapy as first-line therapy. Kaplan-Meier curves and log-rank tests were used to assess OS.
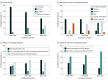
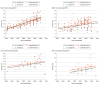
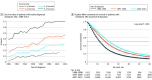
Findings: The literature search identified 150 phase III clinical trials with 77 494 total enrollments, and 67 126 patients with mCRC were identified from the SEER database. Significant increases in survival were noted over time, best reflected in the experimental arm of first-line therapy (OS increased by 5.7 months per 10 years; 95% CI, 4.7-6.6 months; progression-free survival increased by 1.4 months per 10 years; 95% CI, 0.7-2.1 months). Although 69 of 148 trials (46.6%) met their predefined primary end point (including 20 of 44 trials [45.5%] with OS as the primary end point), only 35 of 132 trials (26.5%) resulted in improvement in OS by 2 months or more (including 13 of 42 trials [31.0%] with OS as the primary end point). Multivariable logistic regression showed that third-line therapies or later (odds ratio, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.51-0.63) and funding by pharmaceutical companies (odds ratio, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.54-0.60) were less often associated with improvement in OS. Furthermore, there was a decrease in the novelty of targets and agents over time, with trials that evaluated regimens composed entirely of previously approved drugs for mCRC increasing from 28% to 50%. Data from the SEER database showed that median OS increased from 12 months (95% CI, 12-13 months) (1986-1996) to 21 months (95% CI, 21-22 months) (2007-2015) (P < .001), but the 5-year OS continued to be low at 12.2% in 2011.
Conclusions and relevance: In this systematic review, OS for patients with mCRC appeared to improve significantly in trials, translating into meaningful benefits outside the clinical trial setting; however, these advances, although significant cumulatively, are largely incremental individually. These data should be a call to aim for larger gains from future trials with novel drugs, building on the increasing understanding of the biology of mCRC and sophisticated translational research tools.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Biologic Agents Among Black and White Medicare Patients in the US With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Dec 1;4(12):e2136378. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.36378. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34910154 Free PMC article.
-
Individual patient data analysis of progression-free survival versus overall survival as a first-line end point for metastatic colorectal cancer in modern randomized trials: findings from the analysis and research in cancers of the digestive system database.J Clin Oncol. 2015 Jan 1;33(1):22-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.56.5887. Epub 2014 Nov 10. J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25385741 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of observational studies of trifluridine/tipiracil (TAS-102) for metastatic colorectal cancer.Acta Oncol. 2019 Aug;58(8):1149-1157. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2019.1605192. Epub 2019 Apr 19. Acta Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31002008
-
KRAS Testing for Anti-EGFR Therapy in Advanced Colorectal Cancer: An Evidence-Based and Economic Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(25):1-49. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074403 Free PMC article.
-
Colorectal Cancer Survival Gains and Novel Treatment Regimens: A Systematic Review and Analysis.JAMA Oncol. 2015 Sep;1(6):787-95. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.1790. JAMA Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26181239
Cited by
-
Role of Transhepatic Arterial Radioembolization in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2022 Nov;45(11):1579-1589. doi: 10.1007/s00270-022-03268-y. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2022. PMID: 36104632 Review.
-
PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway as a Target for Colorectal Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 9;25(6):3178. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063178. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highlighting the value of Alzheimer's disease-focused registries: lessons learned from cancer surveillance.Front Aging. 2023 May 5;4:1179275. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2023.1179275. eCollection 2023. Front Aging. 2023. PMID: 37214775 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of fruquintinib in Chinese patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer.Int J Clin Pharm. 2024 Aug;46(4):872-880. doi: 10.1007/s11096-024-01721-1. Epub 2024 Apr 20. Int J Clin Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38642249
-
Recent clinical trials and optical control as a potential strategy to develop microtubule-targeting drugs in colorectal cancer management.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Apr 7;30(13):1780-1790. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i13.1780. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38659489 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, et al. . Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. John Wiley & Sons; 2019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

