MicroRNA-582-3p targeting ribonucleotide reductase regulatory subunit M2 inhibits the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- PMID: 35609318
- PMCID: PMC9275912
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2078026
MicroRNA-582-3p targeting ribonucleotide reductase regulatory subunit M2 inhibits the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Abstract
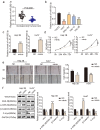
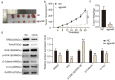
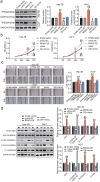
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an important cause of death worldwide. MicroRNA (miRNA)-mediated gene silencing is involved in tumor biology. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the function and mechanism of action of miR-582-3p in HCC. We performed reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting to detect the expression levels of miR-582-3p, ribonucleotide reductase regulatory subunit M2 (RRM2), and markers of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (Wnt, Gsk-3β, β-catenin, and C-myc). The potential binding between miR-582-3p and RRM2 was confirmed using a dual-luciferase reporter assay. The proliferative and migratory capacities of the cells were evaluated using the cell counting kit-8 and wound-healing assays, respectively. Mouse models were used to validate the role of miR-582-3p in vivo. We observed the downregulation of miR-582-3p levels in HCC tumors and cell lines. Its upregulation in Huh7 and Hep 3B cells impaired their proliferation and migration, and the in vivo results showed suppressed tumor growth. Additionally, miR-582-3p upregulation also reduced the expression levels of Wnt, β-catenin, and C-myc, but enhanced the expression levels of glycogen synthase kinase-3β, both in vitro and in vivo. miR-582-3p targeted RRM2, and a negative correlation was observed in its expression patterns in HCC. Furthermore, RRM2 overexpression aggravated the proliferative and migratory capabilities of Hep3B and Huh7 cells and triggered Wnt/β-catenin signaling. However, miR-582-3p depleted RRM2 expression, thereby attenuating the oncogenic effects of RRM2. In conclusion, our results demonstrated that miR-582-3p binds to RRM2 to regulate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, thereby blocking the progression of HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; RRM2; miR-582-3p; wnt/β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
miR-557 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by targeting RAB10.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Feb 15;16(4):3716-3733. doi: 10.18632/aging.205554. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38364252 Free PMC article.
-
A positive feedback loop involving the LINC00346/β-catenin/MYC axis promotes hepatocellular carcinoma development.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020 Feb;43(1):137-153. doi: 10.1007/s13402-019-00478-4. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020. PMID: 31691159
-
MiR-19a-3p regulates the Forkhead box F2-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and affects the biological functions of colorectal cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Feb 14;26(6):627-644. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.627. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32103872 Free PMC article.
-
Klotho: a tumor suppressor and modulator of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Lab Invest. 2016 Feb;96(2):197-205. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.86. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 26237271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in liver biology and tumorigenesis.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024 May;60(5):466-481. doi: 10.1007/s11626-024-00858-7. Epub 2024 Feb 20. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024. PMID: 38379098 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Profiling and Therapeutic Insights into Differentially Expressed Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 30;15(23):5653. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235653. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067357 Free PMC article.
-
hsa_circ_0000285 sponging miR-582-3p promotes neuroblastoma progression by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Open Med (Wars). 2023 Jul 14;18(1):20230726. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0726. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 37465351 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Expression Signatures in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: High-Throughput Searching for Key miRNA Markers in Patients from the Volga-Ural Region of Eurasian Continent.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 7;24(8):6909. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086909. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108073 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the Molecular Complexity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Unveiling Novel Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets Through Advanced Bioinformatics Analysis.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Aug;7(8):e2152. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.2152. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 39118438 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane RRM2-positive cells represent a malignant population with cancer stem cell features in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 6;43(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03174-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39243109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. Epub 2021/02/05. PubMed PMID: 33538338 - PubMed
-
- Konyn P, Ahmed A, Kim D.. Current epidemiology in hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.2021;15(11):1295–1307. Epub 2021/10/09. PubMed PMID: 34624198. - PubMed
-
- Tang A, Hallouch O, Chernyak V, et al. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: target population for surveillance and diagnosis. Abdom Radiol (NY).2018;43(1):13–25. Epub 2017/06/26. PubMed PMID: 28647765. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
