Transcriptome-wide mapping reveals a diverse dihydrouridine landscape including mRNA
- PMID: 35609439
- PMCID: PMC9129914
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001622
Transcriptome-wide mapping reveals a diverse dihydrouridine landscape including mRNA
Abstract
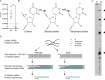
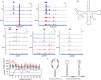
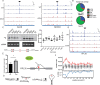
Dihydrouridine is a modified nucleotide universally present in tRNAs, but the complete dihydrouridine landscape is unknown in any organism. We introduce dihydrouridine sequencing (D-seq) for transcriptome-wide mapping of D with single-nucleotide resolution and use it to uncover novel classes of dihydrouridine-containing RNA in yeast which include mRNA and small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA). The novel D sites are concentrated in conserved stem-loop regions consistent with a role for D in folding many functional RNA structures. We demonstrate dihydrouridine synthase (DUS)-dependent changes in splicing of a D-containing pre-mRNA in cells and show that D-modified mRNAs can be efficiently translated by eukaryotic ribosomes in vitro. This work establishes D as a new functional component of the mRNA epitranscriptome and paves the way for identifying the RNA targets of multiple DUS enzymes that are dysregulated in human disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Comment in
-
Expanding the epitranscriptome: Dihydrouridine in mRNA.PLoS Biol. 2022 Jul 20;20(7):e3001720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001720. eCollection 2022 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 35857789 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Expanding the epitranscriptome: Dihydrouridine in mRNA.PLoS Biol. 2022 Jul 20;20(7):e3001720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001720. eCollection 2022 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 35857789 Free PMC article.
-
D-Seq: Genome-wide detection of dihydrouridine modifications in RNA.Methods Enzymol. 2023;692:3-22. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2023.09.001. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Methods Enzymol. 2023. PMID: 37925185
-
The Dihydrouridine landscape from tRNA to mRNA: a perspective on synthesis, structural impact and function.RNA Biol. 2022 Jan;19(1):735-750. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2078094. RNA Biol. 2022. PMID: 35638108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription-wide mapping of dihydrouridine reveals that mRNA dihydrouridylation is required for meiotic chromosome segregation.Mol Cell. 2022 Jan 20;82(2):404-419.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.11.003. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 34798057 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydrouridine in the Transcriptome: New Life for This Ancient RNA Chemical Modification.ACS Chem Biol. 2022 Jul 15;17(7):1638-1657. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00307. Epub 2022 Jun 23. ACS Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 35737906 Review.
Cited by
-
Expanding the epitranscriptome: Dihydrouridine in mRNA.PLoS Biol. 2022 Jul 20;20(7):e3001720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001720. eCollection 2022 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 35857789 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Approaches To Investigate Post-transcriptional RNA Regulation.ACS Chem Biol. 2023 Aug 18;18(8):1684-1697. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.3c00406. Epub 2023 Aug 4. ACS Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37540831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional redundancy in tRNA dihydrouridylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jun 10;52(10):5880-5894. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae325. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38682613 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments, opportunities, and challenges in the study of mRNA pseudouridylation.RNA. 2024 Apr 16;30(5):530-536. doi: 10.1261/rna.079975.124. RNA. 2024. PMID: 38531650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human DUS1L catalyzes dihydrouridine modification at tRNA positions 16/17, and DUS1L overexpression perturbs translation.Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 2;7(1):1238. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06942-8. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39354220 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

