Paving the way to point of care (POC) devices for SARS-CoV-2 detection
- PMID: 35609482
- PMCID: PMC9116970
- DOI: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123542
Paving the way to point of care (POC) devices for SARS-CoV-2 detection
Abstract
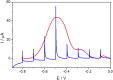
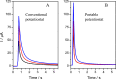
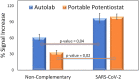
In this work we present a powerful, affordable, and portable biosensor to develop Point of care (POC) SARS-CoV-2 virus detection. It is constructed from a fast, low cost, portable and electronically automatized potentiostat that controls the potential applied to a disposable screen-printed electrochemical platform and the current response. The potentiostat was designed to get the best signal-to-noise ratio, a very simple user interface offering the possibility to be used by any device (computer, mobile phone or tablet), to have a small and portable size, and a cheap manufacturing cost. Furthermore, the device includes as main components, a data acquisition board, a controller board and a hybridization chamber with a final size of 10 × 8 × 4 cm. The device has been tested by detecting specific SARS-CoV-2 virus sequences, reaching a detection limit of 22.1 fM. Results agree well with those obtained using a conventional potentiostat, which validate the device and pave the way to the development of POC biosensors. In this sense, the device has finally applied to directly detect the presence of the virus in nasopharyngeal samples of COVID-19 patients and results confirm its utility for the rapid detection infected samples avoiding any amplification process.
Keywords: Electronically automatized potentiostat; POC biosensor; Portable; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Wu F., Zhao S., Yu B., Chen Y.M., Wang W., Song Z.G., Hu Y., Tao Z.W., Tian J.H., Pei Y.Y., Yuan M.L., Zhang Y.L., Dai F.H., Liu Y., Wang Q.M., Zheng J.J., Xu L., Holmes E.C., Zhang Y.Z. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature. 2020;579:265–269. doi: 10.1038/S41586-020-2008-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Statement on the second meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee regarding the outbreak of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), (n.d.). https://www.who.int/news/item/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-meeting...) (accessed January 4, 2022).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

