The clinical and laboratory diagnosis of vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 35609563
- PMCID: PMC9132380
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022007766
The clinical and laboratory diagnosis of vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia
Abstract
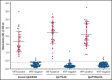
Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) is a rare but serious adverse syndrome occurring 5 to 30 days after adenoviral vector COVID-19 vaccination. Therefore, a practical evaluation of clinical assessments and laboratory testing for VITT is needed to prevent significant adverse outcomes as the global use of adenoviral vector vaccines continues. We received the clinical information and blood samples of 156 patients in Canada with a suspected diagnosis of VITT between April and July 2021. The performance characteristics of various diagnostic laboratory tests were evaluated against the platelet factor 4 (PF4)-14C-serotonin release assay (SRA) including a commercial anti-PF4/heparin immunoglobulin G (IgG)/IgA/IgM enzyme immunoassay (EIA, PF4 Enhanced; Immucor), in-house IgG-specific anti-PF4 and anti-PF4/heparin-EIAs, the standard SRA, and the PF4/heparin-SRA. Of those, 43 (27.6%) had serologically confirmed VITT-positive based on a positive PF4-SRA result and 113 (72.4%) were VITT-negative. The commercial anti-PF4/heparin EIA, the in-house anti-PF4-EIA, and anti-PF4/heparin-EIA were positive for all 43 VITT-confirmed samples (100% sensitivity) with a few false-positive results (mean specificity, 95.6%). These immunoassays had specificities of 95.6% (95% confidence interval [CI], 90.0-98.6), 96.5% (95% CI, 91.2-99.0), and 97.4% (95% CI, 92.4-99.5), respectively. Functional tests, including the standard SRA and PF4/heparin-SRA, had high specificities (100%), but poor sensitivities for VITT (16.7% [95% CI, 7.0-31.4]; and 46.2% [95% CI, 26.6-66.6], respectively). These findings suggest EIA assays that can directly detect antibodies to PF4 or PF4/heparin have excellent performance characteristics and may be useful as a diagnostic test if the F4-SRA is unavailable.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Joint CDC and FDA Statement on Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 Vaccine. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/joint-cdc-and-fda-st.... Accessed 15 June 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

