Decreased expression of ErbB2 on left ventricular epicardial cells in patients with diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 35609807
- PMCID: PMC9671200
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110360
Decreased expression of ErbB2 on left ventricular epicardial cells in patients with diabetes mellitus
Abstract
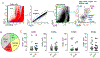
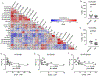
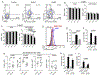
We investigated the cell surface expression of ErbB receptors on left ventricular (LV) epicardial endothelial cells and CD105+ cells obtained from cardiac biopsies of patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting surgery (CABG). Endothelial cells and CD105+ non-endothelial cells were freshly isolated from LV epicardial biopsies obtained from 15 subjects with diabetes mellitus (DM) and 8 controls. The expression of ErbB receptors was examined using flow cytometry. We found that diabetes mellitus (DM) and high levels of hemoglobin A1C are associated with reduced expression of ErbB2. To determine if the expression of ErbB2 receptors is regulated by glucose levels, we examined the effect of high Glucose in human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) and CD105+ non-endothelial cells, using a novel flow cytometric approach to simultaneously determine the total level, cell surface expression, and phosphorylation of ErbB2. Incubation of cells in the presence of 25 mM d-glucose resulted in decreased cell surface but not total levels of ErbB2. The level of ErbB2 at the cell surface is controlled by disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 10 (ADAM10) that is expressed on LV epicardial cells. Inhibition of ADAM10 prevented the high glucose-dependent decrease in the cell surface expression of ErbB2. We suggest that high Glucose depresses ErbB receptor signaling in endothelial cells and cardiac progenitor cells via the promotion of ADAM10-dependent cleavage of ErbB2 at the cell surface, thus contributing to vascular dysfunction and adverse remodeling seen in diabetic patients.
Keywords: ADAM10; Diabetes mellitus; ErbB receptors; Hemoglobin A1C; LV epicardial cells.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
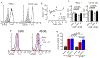
Similar articles
-
ErbB2 promotes endothelial phenotype of human left ventricular epicardial highly proliferative cells (eHiPC).J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018 Feb;115:39-50. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.12.013. Epub 2017 Dec 29. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29291395 Free PMC article.
-
Type 1 diabetes mellitus abrogates compensatory augmentation of myocardial neuregulin-1β/ErbB in response to myocardial infarction resulting in worsening heart failure.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013 Mar 27;12:52. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-52. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013. PMID: 23530877 Free PMC article.
-
The dual targeting of EGFR and ErbB2 with the inhibitor Lapatinib corrects high glucose-induced apoptosis and vascular dysfunction by opposing multiple diabetes-induced signaling changes.J Drug Target. 2015;23(6):506-18. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2015.1057150. Epub 2015 Jun 26. J Drug Target. 2015. PMID: 26114862
-
The vulnerability of the heart as a pluricellular paracrine organ: lessons from unexpected triggers of heart failure in targeted ErbB2 anticancer therapy.Circ Res. 2010 Jan 8;106(1):35-46. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.205906. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 20056944 Review.
-
Cardiotoxicity in signal transduction therapeutics: erbB2 antibodies and the heart.Semin Oncol. 2001 Oct;28(5 Suppl 16):18-26. doi: 10.1016/s0093-7754(01)90278-7. Semin Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11706392 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioinformatics and Next-Generation Data Analysis for Identification of Genes and Molecular Pathways Involved in Subjects with Diabetes and Obesity.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Feb 7;59(2):309. doi: 10.3390/medicina59020309. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 36837510 Free PMC article.
-
ALK1 Signaling in Human Cardiac Progenitor Cells Promotes a Pro-angiogenic Secretome.J Cell Signal. 2024;5(3):122-142. doi: 10.33696/signaling.5.119. J Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 39430425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Emani S RB, Sodha NR, Li J, Bianchi C, Sellke FW. Increased vascular permeability after cardiopulmonary bypass in patients with diabetes is associated with increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and hepatocyte growth factor. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009;138:185–91. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abuelgasim E SS, Abuelgasim B, Soni N, Thomas A, Elgasim M, Harky A. Clinical overview of diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for cardiovascular death. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2021;22:301–314. - PubMed
-
- Halkos ME LO, Puskas JD, Kilgo P, Cooper WA, Morris CD, Guyton RA, Thourani VH. Elevated preoperative hemoglobin A1c level is associated with reduced long-term survival after coronary artery bypass surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;86:1431–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

