Evaluation of the stability of temocillin in elastomeric infusion devices used for outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy in accordance with the requirements of the UK NHS Yellow Cover Document
- PMID: 35609967
- PMCID: PMC10086727
- DOI: 10.1136/ejhpharm-2022-003286
Evaluation of the stability of temocillin in elastomeric infusion devices used for outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy in accordance with the requirements of the UK NHS Yellow Cover Document
Abstract
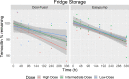
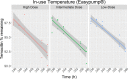
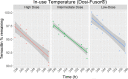
Objective: To evaluate the stability of temocillin solution in two elastomeric infusion devices - Easypump II LT 270-27- S and Dosi-Fusor L25915-250D1 for OPAT administration during 14 days of 5°C±3°C fridge storage followed by 24 hour exposure at an in-use temperature of 32°C, when reconstituted with 0.3% citrate buffer at pH7.
Methods: Stability testing was conducted in accordance with standard protocols in the UK National Health Service Yellow Cover Document (YCD). A stability indicating assay method was applied using a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system with a photodiode array detector. Low (500 mg/240 mL), intermediate (4000 mg/240 mL) and high (6000 mg/240 mL) temocillin concentrations were tested in triplicate devices with duplicate samples taken at 11 time points during fridge storage and subsequent in-use temperature exposure.
Result: The percentage of temocillin remaining after 14 days of fridge storage was greater than 97% in both devices and at all concentrations tested. During subsequent in-use temperature exposure, a 95% stability limit was achieved for 12 hours except for the high concentration (25 mg/mL) in the Dosi-Fusor device. It met this criterion for only 10 hours - the percent of temocillin remaining at 12 hours was 94.5%. However, for all devices and the doses tested, the degradation of temocillin was <9% at the end of 24 hours in-use temperature exposure.
Conclusion: Temocillin reconstituted with 0.3% citrate buffer at pH7 in elastomeric infusion devices can be stored in a fridge (2°C-8°C) for 14 days meeting the YCD acceptance criteria. Considering <5% degradation, the current data supports twice daily dosing of temocillin within the OPAT setting. In jurisdictions where a <10% degradation limit is acceptable, once daily dosing with 24-hour continuous infusion may be considered. Temocillin is a useful alternative to other broad-spectrum anti-Gram-negative agents currently utilised in the OPAT setting and supports the wider antimicrobial stewardship agenda.
Keywords: Administration, Intravenous; Drug Compounding; Drug Monitoring; Pharmacology; Quality Assurance, Health Care.
© European Association of Hospital Pharmacists 2023. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
